On the Efficiency of Individualized Theta/Beta Ratio Neurofeedback Combined with Forehead EMG Training in ADHD Children
- PMID: 29403368
- PMCID: PMC5785729
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00003
On the Efficiency of Individualized Theta/Beta Ratio Neurofeedback Combined with Forehead EMG Training in ADHD Children
Abstract
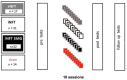
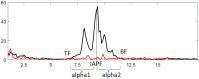
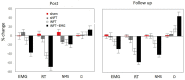
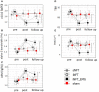
Background: Neurofeedback training (NFT) to decrease the theta/beta ratio (TBR) has been used for treating hyperactivity and impulsivity in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD); however, often with low efficiency. Individual variance in EEG profile can confound NFT, because it may lead to influencing non-relevant activity, if ignored. More importantly, it may lead to influencing ADHD-related activities adversely, which may even result in worsening ADHD symptoms. Electromyogenic (EMG) signal resulted from forehead muscles can also explain the low efficiency of the NFT in ADHD from both practical and psychological point-of-view. The first aim of this study was to determine EEG and EMG biomarkers most related to the main ADHD characteristics, such as impulsivity and hyperactivity. The second aim was to confirm our hypothesis that the efficiency of the TBR NFT can be increased by individual adjustment of the frequency bands and simultaneous training on forehead muscle tension. Methods: We recruited 94 children diagnosed with ADHD (ADHD) and 23 healthy controls (HC). All participants were male and aged between six and nine. Impulsivity and attention were assessed with Go/no-Go task and delayed gratification task, respectively; and 19-channel EEG and forehead EMG were recorded. Then, the ADHD group was randomly subdivided into (1) standard, (2) individualized, (3) individualized+EMG, and (4) sham NFT (control) groups. The groups were compared based on TBR and EEG alpha activity, as well as hyperactivity and impulsivity three times: pre-NFT, post-NFT and 6 months after the NFT (follow-up). Results: ADHD children were characterized with decreased individual alpha peak frequency, alpha bandwidth and alpha amplitude suppression magnitude, as well as with increased alpha1/alpha2 (a1/a2) ratio and scalp muscle tension when c (η2 ≥ 0.212). All contingent TBR NFT groups exhibited significant NFT-related decrease in TBR not evident in the control group. Moreover, we detected a higher overall alpha activity in the individualized but not in the standard NFT group. Mixed MANOVA considering between-subject factor GROUP and within-subject factor TIME showed that the individualized+EMG group exhibited the highest level of clinical improvement, which was associated with increase in the individual alpha activity at the 6 months follow-up when comparing with the other approaches (post hoc t = 3.456, p = 0.011). Conclusions: This study identified various (adjusted) alpha activity metrics as biomarkers with close relationship with ADHD symptoms, and demonstrated that TBR NFT individually adjusted for variances in alpha activity is more successful and clinically more efficient than standard, non-individualized NFT. Moreover, these training effects of the individualized TBR NFT lasted longer when combined with EMG.
Keywords: ADHD; EMG; individual alpha activity; neurofeedback training; theta/beta ratio.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edn. Arlington, TX: American Psychiatric Publishing, 59–65.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

