A Hybrid Model for Safety Pharmacology on an Automated Patch Clamp Platform: Using Dynamic Clamp to Join iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes and Simulations of Ik1 Ion Channels in Real-Time
- PMID: 29403387
- PMCID: PMC5782795
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01094
A Hybrid Model for Safety Pharmacology on an Automated Patch Clamp Platform: Using Dynamic Clamp to Join iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes and Simulations of Ik1 Ion Channels in Real-Time
Abstract
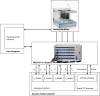
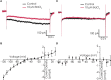
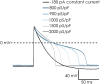
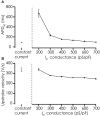
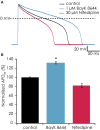
An important aspect of the Comprehensive In Vitro Proarrhythmia Assay (CiPA) proposal is the use of human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes and the confirmation of their predictive power in drug safety assays. The benefits of this cell source are clear; drugs can be tested in vitro on human cardiomyocytes, with patient-specific genotypes if needed, and differentiation efficiencies are generally excellent, resulting in a virtually limitless supply of cardiomyocytes. There are, however, several challenges that will have to be surmounted before successful establishment of hSC-CMs as an all-round predictive model for drug safety assays. An important factor is the relative electrophysiological immaturity of hSC-CMs, which limits arrhythmic responses to unsafe drugs that are pro-arrhythmic in humans. Potentially, immaturity may be improved functionally by creation of hybrid models, in which the dynamic clamp technique joins simulations of lacking cardiac ion channels (e.g., IK1) with hSC-CMs in real-time during patch clamp experiments. This approach has been used successfully in manual patch clamp experiments, but throughput is low. In this study, we combined dynamic clamp with automated patch clamp of iPSC-CMs in current clamp mode, and demonstrate that IK1 conductance can be added to iPSC-CMs on an automated patch clamp platform, resulting in an improved electrophysiological maturity.
Keywords: automated patch clamp electrophysiology; cardiomyocyte; dynamic clamp; inward rectifying potassium ion channels; safety pharmacology; stem cell.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated Dynamic Clamp for Simulation of IK1 in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes in Real Time Using Patchliner Dynamite8.Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;88(1):e70. doi: 10.1002/cpph.70. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31868992
-
Recording of multiple ion current components and action potentials in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes via automated patch-clamp.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2019 Nov-Dec;100:106599. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2019.106599. Epub 2019 Jun 20. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2019. PMID: 31228558
-
Establishment of an automated patch-clamp platform for electrophysiological and pharmacological evaluation of hiPSC-CMs.Stem Cell Res. 2019 Dec;41:101662. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2019.101662. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Stem Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31809994
-
Dynamic Clamp in Electrophysiological Studies on Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes-Why and How?J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;77(3):267-279. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000955. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33229908 Review.
-
The immature electrophysiological phenotype of iPSC-CMs still hampers in vitro drug screening: Special focus on IK1.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Mar;183:127-136. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 28986101 Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of Dynamic Clamp to Cardiac Arrhythmia Research: Role in Drug Target Discovery and Safety Pharmacology Testing.Front Physiol. 2018 Jan 4;8:1099. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01099. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29354069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recognition of high-specificity hERG K+ channel inhibitor-induced arrhythmia in cardiomyocytes by automated template matching.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2021 Mar 16;7:24. doi: 10.1038/s41378-021-00251-4. eCollection 2021. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2021. PMID: 34567738 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation into the difference in mitochondrial-cytosolic calcium coupling between adult cardiomyocyte and hiPSC-CM using a novel multifunctional genetic probe.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Mar;473(3):447-459. doi: 10.1007/s00424-021-02524-3. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 33587181 Free PMC article.
-
Light-Activated Dynamic Clamp Using iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes.Biophys J. 2018 Dec 4;115(11):2206-2217. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.10.018. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 30447994 Free PMC article.
-
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes as an electrophysiological model: Opportunities and challenges-The Hamburg perspective.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1132165. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1132165. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36875015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blinova K., Stohlman J., Vicente J., Chan D., Johannesen L., Hortigon-Vinagre M. P., et al. . (2017). Comprehensive translational assessment of human-induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes for evaluating drug-induced arrhythmias. Toxicol. Sci. 155, 234–247. 10.1093/toxsci/kfw200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

