Validation and application by HPLC for simultaneous determination of vitexin-2″-O-glucoside, vitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside, rutin, vitexin, and hyperoside
- PMID: 29403712
- PMCID: PMC5760805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2011.09.003
Validation and application by HPLC for simultaneous determination of vitexin-2″-O-glucoside, vitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside, rutin, vitexin, and hyperoside
Abstract
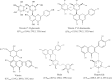
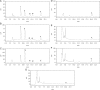
A simple, precise, and rapid high-performance liquid chromatographic method was developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of vitexin-2″-O-glucoside, vitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside, rutin, vitexin, and hyperoside. The HPLC separation was performed using a Shim-pack VP-ODS C18 column (250 mm×4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm) with the isocratic mobile phase consisting of tetrahydrofuran/ acetonitrile/0.05% phosphoric acid solution (20:3:77, v/v/v), and the flow rate was set at 1.0 mL/min. UV detection was carried out at a wavelength of 360 nm and the whole analysis took 25 min. The method was linear in the range of 4.12-206.00 μg/mL for vitexin-2″-O-glucoside, 4.05-202.50 μg/mL for vitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside, 1.64-82.00 μg/mL for rutin, 1.74-87.00 μg/mL for vitexin, and 1.41-70.60 μg/mL for hyperoside with the correlation coefficient for each analyte more than 0.998. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) were 0.6 and 2 ng for vitexin-2″-O-glucoside, 0.6 and 2 ng for vitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside, 0.3 and 1 ng for rutin, 1 and 3 ng for vitexin, and 0.5 and 2 ng for hyperoside, respectively. Intra- and inter-day precision and accuracy (RSD) were less than 3%. The developed HPLC method was successfully applied to the analysis of five flavonoids in hawthorn leaves, hawthorn fruits, and the preparations containing hawthorn leaves or fruits.
Keywords: Flavonoids; Hawthorn; High-performance liquid chromatography; Leaves and fruits; Preparations.
Figures
References
-
- Rigelsky J.M., Sweet B.V. Hawthorn: pharmacology and therapeutic uses. American Journal of Health System Pharmacy. 2002;59:417–422. - PubMed
-
- Chen J.D., Wu Y.Z., Tao Z.L. Hawthorn (shan zha) drink and its lowering effect on blood lipid levels in humans and rats. World Review of Nutrition and Dietics. 1995;77:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Kao E.S., Wang C.J., Lin W.L. Anti-inflammatory potential of flavonoid contents from dried fruit of Crataegus pinnatifida in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2005;53:430–436. - PubMed
-
- Pietta P., Manera E., Ceva P. Isocratic liquid-chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of Passiflora incarnata L. and Crataegus monogyna flavonoids in drugs. Journal of Chromatography A. 1986;357:233–238. - PubMed
-
- Müller A., Linke W., Zhao Y. Crataegus extract prolongs action potential duration in guinea-pig papillary muscle. Phytomedicine. 1996;3:257–261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

