Immobilized enzyme reactors in HPLC and its application in inhibitor screening: A review
- PMID: 29403726
- PMCID: PMC5760896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2011.12.002
Immobilized enzyme reactors in HPLC and its application in inhibitor screening: A review
Abstract
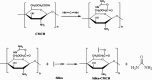
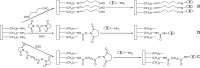
This paper sets out to summarize the literatures based on immobilized enzyme bio-chromatography and its application in inhibitors screening in the last decade. In order to screen enzyme inhibitors from a mass of compounds in preliminary screening, multi-pore materials with good biocompatibility are used for the supports of immobilizing enzymes, and then the immobilized enzyme reactor applied as the immobilized enzyme stationary phase in HPLC. Therefore, a technology platform of high throughput screening is gradually established to screen the enzyme inhibitors as new anti-tumor drugs. Here, we briefly summarize the selective methods of supports, immobilization techniques, co-immobilized enzymes system and the screening model.
Keywords: Immobilized enzyme reactors (IMERs); Molecular bio-chromatography; Screening enzyme inhibitors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tyrosinase immobilized enzyme reactor: development and evaluation.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Jan 15;945-946:10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.11.042. Epub 2013 Nov 25. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24317418
-
Drug affinity to immobilized target bio-polymers by high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003 Nov 25;797(1-2):111-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.08.033. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 14630146 Review.
-
Immobilization of NTPDase-1 from Trypanosoma cruzi and Development of an Online Label-Free Assay.J Anal Methods Chem. 2016;2016:9846731. doi: 10.1155/2016/9846731. Epub 2016 Dec 14. J Anal Methods Chem. 2016. PMID: 28070446 Free PMC article.
-
A strategy for screening trypsin inhibitors from traditional Chinese medicine based on a monolithic capillary immobilized enzyme reactor coupled with offline liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry.J Sep Sci. 2019 Jun;42(11):1980-1989. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201900169. Epub 2019 Apr 24. J Sep Sci. 2019. PMID: 30945464
-
Particle-based immobilized enzymatic reactors in microfluidic chips.Talanta. 2018 Apr 1;180:211-228. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.12.043. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Talanta. 2018. PMID: 29332803 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of Liposome Formulations for CRISPR/Cas9 Enzyme Immobilization: Evaluation of 5-Alpha-Reductase Enzyme Knockout for Androgenic Disorders.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 20;8(48):46101-46112. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07138. eCollection 2023 Dec 5. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38075788 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme Engineering: Performance Optimization, Novel Sources, and Applications in the Food Industry.Foods. 2024 Nov 28;13(23):3846. doi: 10.3390/foods13233846. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39682920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Girelli A.M., Mattei E. Application of immobilized enzyme reactor in on-line high performance liquid chromatography: a review. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005;819(1):3–16. - PubMed
-
- Nei Y.L., Wang W.H. Immobilized enzyme reactor in on-line LC and its application in drug screening. Chromatographia. 2009;69:S5–S12.
-
- Ma J.F., Zhang L.H., Zhen L. Immobilized enzyme reactors in proteomics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011;30(5):691–702.
-
- Núñez O., Nakanishi K., Tanaka N. Preparation of monolithic silica columns for high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2008;1191(1–2):231–252. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki S., Takahashi M., Ohira M. Monolithic silica rod columns for high-efficiency reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2011;1218(15):1988–1994. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

