Monitoring the hydrolyzation of aspirin during the dissolution testing for aspirin delayed-release tablets with a fiber-optic dissolution system
- PMID: 29403772
- PMCID: PMC5760771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2012.06.002
Monitoring the hydrolyzation of aspirin during the dissolution testing for aspirin delayed-release tablets with a fiber-optic dissolution system
Abstract
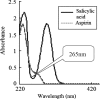
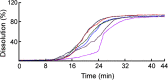
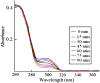
The purpose of this study was to investigate the hydrolyzation of aspirin during the process of dissolution testing for aspirin delayed-release tablets. Hydrolysis product of salicylic acid can result in adverse effects and affect the determination of dissolution rate assaying. In this study, the technique of differential spectra was employed, which made it possible to monitor the dissolution testing in situ. The results showed that the hydrolyzation of aspirin made the percentage of salicylic acid exceed the limit of free salicylic acid (4.0), and the hydrolyzation may affect the quality detection of aspirin delayed-release tablets.
Keywords: Aspirin delayed-release tablets; Drug dissolution test; Fiber-optic dissolution system; UV–vis spectrum.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multivariate approaches for the development of quality control in-situ fiber optics dissolution methods for fixed-dose combination tablets.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Jun;45(6):999-1008. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2019.1593435. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30905176
-
Effect of tablet integrity on the dissolution rate of sustained-release preparations.J Clin Pharm Ther. 1996 Jun;21(3):155-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.1996.tb00015.x. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1996. PMID: 8873848
-
Aspirin--a national survey V: Determination of aspirin and impurities in enteric coated tablets and suppository formulations and in vitro dissolution of enteric coated tablets.J Pharm Sci. 1982 Sep;71(9):1049-52. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710923. J Pharm Sci. 1982. PMID: 7131273
-
Simultaneous determination of salicylic acid and acetylsalicylic acid in aspirin delayed-release tablet formulations by second-derivative UV spectrophotometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1998 Dec;18(4-5):871-5. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(98)00225-8. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1998. PMID: 9919990
-
Attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy (ATR-IR) as an in situ technique for dissolution studies.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010 Nov 2;53(3):269-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2010.04.023. Epub 2010 Apr 27. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010. PMID: 20493652
Cited by
-
Spider diagram and sustainability evaluation of UV-methods strategy for quantification of aspirin and sildenafil citrate in the presence of salicylic acid in their bulk and formulation.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 5;9(4):e15260. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15260. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37123917 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of UV Light on Photodegradation of Acetylsalicylic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 14;22(8):4046. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084046. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919943 Free PMC article.
-
Nanofiller-Enhanced Soft Non-Gelatin Alginate Capsules for Modified Drug Delivery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Apr 13;14(4):355. doi: 10.3390/ph14040355. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924320 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Processing Parameters on the Quality of Pharmaceutical Solid Dosage Forms Produced by Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).Pharmaceutics. 2019 Nov 27;11(12):633. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11120633. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31783633 Free PMC article.
-
Portable and automated analyzer for rapid and high precision in vitro dissolution of drugs.J Pharm Anal. 2021 Aug;11(4):490-498. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Pharm Anal. 2021. PMID: 34513125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan A., Rahman M., Islam S. Antipyretic activity of Peperomia pellucida leaves in rabbit. Turk. J. Biol. 2008;1(32):37–41.
-
- Erkan D., Harrison M.J., Levy R. Aspirin for primary thrombosis prevention in the antiphospholipid syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in asymptomatic antiphospholipid antibody-positive individuals. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(7):2382–2391. - PubMed
-
- Sørensen H.T., Mellemkjaer L., Blot W.J. Risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding associated with use of low-dose aspirin. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000;95(9):2218–2224. - PubMed
-
- Berges-Gimeno M.P., Stevenson D.D. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced reactions and desensitization. J. Asthma. 2004;41(4):375–384. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources