Chromatographic fingerprinting and quantitative analysis for the quality evaluation of Xinkeshu tablet
- PMID: 29403777
- PMCID: PMC5760917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2012.05.006
Chromatographic fingerprinting and quantitative analysis for the quality evaluation of Xinkeshu tablet
Abstract
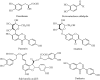
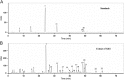
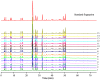
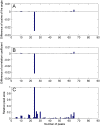
A simple, sensitive and accurate method based on high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with diode array detector (DAD) was developed and validated for systematic quality evaluation of one type of traditional Chinese medicine preparations named Xinkeshu (XKS) tablet. In this study, the chromatographic fingerprints of XKS tablet were developed first, 23 peaks were selected as the common peaks to evaluate the similarities among different batches of XKS samples, which were manufactured in a long time span of three years. Additionally, simultaneous quantification of six markers in XKS tablet, including Danshensu, Protocatechuic aldehyde, Puerarin, Daidzin, Salvianolic acid B and Daidzein, was performed. The validation results showed that the developed method was specific, accurate, precise and robust. The preliminary explanation on why a close similarity between fingerprints did not exactly mean similar contents of chemical components in samples was given. The contribution of each chromatographic peak to similarity was also evaluated. The developed method offers an efficient, reliable and practical approach for systematic quality evaluation of XKS tablet.
Keywords: Fingerprint analysis; High-performance liquid chromatography; Multi-ingredient quantitative analysis; Quality evaluation; Xinkeshu tablet.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Useful Strategy to Evaluate the Quality Consistency of Traditional Chinese Medicines Based on Liquid Chromatography and Chemometrics.J Anal Methods Chem. 2015;2015:589654. doi: 10.1155/2015/589654. Epub 2015 Nov 4. J Anal Methods Chem. 2015. PMID: 26618023 Free PMC article.
-
Quality evaluation of Huaijiao pill by chromatographic fingerprint and simultaneous determination of its major bioactive components.J Pharm Anal. 2016 Aug;6(4):249-255. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 15. J Pharm Anal. 2016. PMID: 29403990 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the major constituents in Chinese medicinal preparation Dan-Lou tablet by ultra high performance liquid chromatography/diode-array detector/quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Jun;80:50-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.02.011. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23518306
-
Novel strategy for quality consistency evaluation of Chinese medicine "YIQING" tablet that combines the simultaneous quantification and screening of ten bioactive constituents.J Sep Sci. 2017 Aug;40(15):3064-3073. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201700291. Epub 2017 Jun 28. J Sep Sci. 2017. PMID: 28590083 Review.
-
Quickly quantifying the dissolution fingerprints of compound Danshen dropping pill by HPLC.Ann Transl Med. 2013 Jul;1(2):16. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2013.03.03. Ann Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 25332960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel method HPLC-DAD analysis of the Contentsof Moutan Cortexand Paeoniae Radix Alba with similar constituents-monoterpene glycosides in Guizhi Fuling Wan.Molecules. 2014 Nov 4;19(11):17957-67. doi: 10.3390/molecules191117957. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25375336 Free PMC article.
-
Leaves of Invasive Plants-Japanese, Bohemian and Giant Knotweed-The Promising New Source of Flavan-3-ols and Proanthocyanidins.Plants (Basel). 2020 Jan 17;9(1):118. doi: 10.3390/plants9010118. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31963589 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Jianpi Qingre Tongluo Recipe in Reducing Inflammation and Dyslipidemia in Osteoarthritis via Lnc RNA HOTAIR/APN/PI3K/AKT.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Jul 26;17:3293-3318. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S466148. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39081673 Free PMC article.
-
A Useful Strategy to Evaluate the Quality Consistency of Traditional Chinese Medicines Based on Liquid Chromatography and Chemometrics.J Anal Methods Chem. 2015;2015:589654. doi: 10.1155/2015/589654. Epub 2015 Nov 4. J Anal Methods Chem. 2015. PMID: 26618023 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Strategy to Identify and Quantify the Quality Markers of Xinkeshu Tablets Based on Spectrum-Effect Relationship, Network Pharmacology, Plasma Pharmacochemistry, and Pharmacodynamics of Zebrafish.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 23;13:899038. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.899038. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35677447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie P.S., Leung A.Y. Understanding the traditional aspect of Chinese medicine in order to achieve meaningful quality control of Chinese materia medica. J. Chromatogr. A. 2009;1216(11):1933–1940. - PubMed
-
- Qiu J. China plans to modernize traditional medicine. Nature. 2007;446(7136):590–591. - PubMed
-
- Liang Y.Z., Xie P., Chan K. Quality control of herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. B. 2004;812(1-2):53–70. - PubMed
-
- Liang X.M., Jin Y., Wang Y.P. Qualitative and quantitative analysis in quality control of traditional Chinese medicines. J. Chromatogr. A. 2009;1216(11):2033–2044. - PubMed
-
- Xie P., Chen S., Liang Y.Z. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis—a rational approach for quality assessment of traditional Chinese herbal medicine. J. Chromatogr. A. 2006;1112(1-2):171–180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

