Simultaneous quantification of prodrug oseltamivir and its metabolite oseltamivir carboxylate in human plasma by LC-MS/MS to support a bioequivalence study
- PMID: 29403810
- PMCID: PMC5760963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2012.11.004
Simultaneous quantification of prodrug oseltamivir and its metabolite oseltamivir carboxylate in human plasma by LC-MS/MS to support a bioequivalence study
Abstract
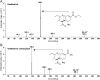
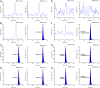
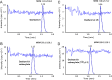
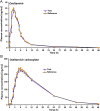
A simple, precise and rapid liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method has been developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate, a neuraminidase inhibitor, using their deuterated analogs as internal standards (ISs). The method involved solid phase extraction of the analytes and ISs from 200 μL human plasma with no reconstitution and drying steps. The chromatographic separation was achieved on a Symmetry C18 (100 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm) column using 10 mM ammonium formate and acetonitrile (30:70, v/v) as the mobile phase in a run time of 2.0 min. Quantitation of analytes and ISs were done by multiple reaction monitoring on a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer in the positive ionization mode. The linearity of the method was established in the concentration range of 0.5-200 ng/mL and 2.0-800 ng/mL for oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate respectively. The mean extraction recovery for oseltamivir (94.4%) and oseltamivir carboxylate (92.7%) from spiked plasma samples was consistent and reproducible. The application of this method was demonstrated by a bioequivalence study in 42 healthy Indian subjects with 75 mg oseltamivir phosphate capsules. The assay reproducibility was established by reanalysis of 151 incurred subject samples.
Keywords: Bioequivalence study; Human plasma; LC-MS/MS; Oseltamivir; Oseltamivir carboxylate.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous analysis of oxybutynin and its active metabolite N-desethyl oxybutynin in human plasma by stable isotope dilution LC-MS/MS to support a bioequivalence study.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Oct;84:244-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23867086
-
In vitro and in vivo stability of oseltamivir within a bioequivalence trial.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016 May;408(14):3891-7. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9483-2. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016. PMID: 27002612
-
Development and validation of a high-throughput and robust LC-MS/MS with electrospray ionization method for simultaneous quantitation of oseltamivir phosphate and its oseltamivir carboxylate metabolite in human plasma for pharmacokinetic studies.Biomed Chromatogr. 2011 Jun;25(6):727-33. doi: 10.1002/bmc.1509. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Biomed Chromatogr. 2011. PMID: 20845365
-
Quantitative determination of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate in human fluoride EDTA plasma including the ex vivo stability using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012 Apr 1;891-892:57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.02.026. Epub 2012 Feb 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22418071
-
Validation and reproducibility of an LC-MS/MS method for emixustat and its three deaminated metabolites in human plasma.Bioanalysis. 2018 Nov 1;10(22):1803-1817. doi: 10.4155/bio-2018-0159. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Bioanalysis. 2018. PMID: 30325202 Review.
Cited by
-
A phase I, single-center, randomized, open-label, three-period crossover study to evaluate the drug-drug interaction between ZSP1273 and oseltamivir in healthy Chinese subjects.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Apr 2;69(4):e0172924. doi: 10.1128/aac.01729-24. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39992105 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Selective and rapid determination of raltegravir in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in the negative ionization mode.J Pharm Anal. 2015 Apr;5(2):101-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 23. J Pharm Anal. 2015. PMID: 29403921 Free PMC article.
-
A novel method to estimate the absorption rate constant for two-compartment model fitted drugs without intravenous pharmacokinetic data.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 4;14:1087913. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1087913. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37214472 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of mycophenolic acid in human plasma by ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Anal. 2014 Jun;4(3):205-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 12. J Pharm Anal. 2014. PMID: 29403884 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a sensitive and rapid method for quantitation of (S)-(-)- and (R)-(+)-metoprolol in human plasma by chiral LC-ESI-MS/MS.J Pharm Anal. 2014 Feb;4(1):63-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Mar 5. J Pharm Anal. 2014. PMID: 29403869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moscona A. Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza. New Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:1363–1373. - PubMed
-
- He G.Z., Massarella J.W., Ward P. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the prodrug oseltamivir and its active metabolite Ro 64-0802. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999;37:471–484. - PubMed
-
- Dutkowski R., Smith J.R., Davies B.E. Safety and pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir at standard and high doses. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2010;35:461–467. - PubMed
-
- Schentag J.J., Hill G., Chu T. Similarity in pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate in Japanese and Caucasian subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007;47:689–696. - PubMed
-
- Massarella J.W., He G.Z., Dorr A. The pharmacokinetics and tolerability of the oral neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir (Ro 64-0796/GS4104) in healthy adult and elderly volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000;40:836–843. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

