Application of LC-MS/MS for quantitative analysis of glucocorticoids and stimulants in biological fluids
- PMID: 29403837
- PMCID: PMC5760999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.03.005
Application of LC-MS/MS for quantitative analysis of glucocorticoids and stimulants in biological fluids
Abstract
Liquid chromatography tandem mass chromatography (LC-MS/MS) is an important hyphenated technique for quantitative analysis of drugs in biological fluids. Because of high sensitivity and selectivity, LC-MS/MS has been used for pharmacokinetic studies, metabolites identification in the plasma and urine. This manuscript gives comprehensive analytical review, focusing on chromatographic separation approaches (column packing materials, column length and mobile phase) as well as different acquisition modes (SIM, MRM) for quantitative analysis of glucocorticoids and stimulants. This review is not meant to be exhaustive but rather to provide a general overview for detection and confirmation of target drugs using LC-MS/MS and thus useful in the doping analysis, toxicological studies as well as in pharmaceutical analysis.
Keywords: Biological fluid; Glucocorticoids; Hyphenated techniques; Ionization techniques; LC–MS/MS; Stimulants.
Figures
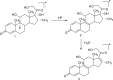
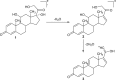
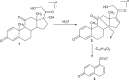
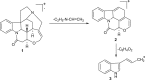

References
-
- Perrenoud L., Saugy M., Saudan C. Detection in urine of 4-methyl-2-hexaneamine a doping agent. J. Chromatogr. B. 2009;877(29):3767–3770. - PubMed
-
- C. Judkins, D. Hall, K. Hoffman, Investigation into Supplement Contamination Levels in the US Market, HFL. 2007. Available from: 〈http://www.supplementsafetynow.com/HFL-supplement-research-report.pdf〉.
-
- Savaliya A.A., Prasad B., Raijada D.K. Detection and characterization of synthetic steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Indian ayurvedic/herbal products using LC–MS/TOF. Drug Test Anal. 2009;1(8):372–381. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S., Riaz M. Quantitation of corticosteroids as common adulterants in local drugs by HPLC. Chromatographia. 1991;31(1–2):67–70.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

