Rapid sensitive validated UPLC-MS method for determination of venlafaxine and its metabolite in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic study
- PMID: 29403857
- PMCID: PMC5761014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.05.002
Rapid sensitive validated UPLC-MS method for determination of venlafaxine and its metabolite in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic study
Abstract
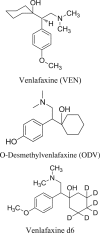
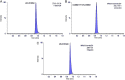
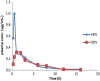
A new ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/ESI) method for simultaneous determination of venlafaxine (VEN) and its metabolite O-desmethylvenlafaxine (ODV) in rat plasma has been developed and validated using Venlafaxine d6 as the internal standard. The compounds and internal standard were extracted from plasma by solid phase extraction. The UPLC separation of the analytes was performed on ACQUITY UPLC® BEH Shield RP18 (1.7 µm, 100 mm×2.1 mm) column, using isocratic elution with mobile phase constituted of water (containing 2 mM ammonium acetate): acetonitrile (20:80, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. All of the analytes were eluted within 1.5 min. The compounds were ionized in the electrospray ionization (ESI) ion source of the mass spectrometer, operating in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) and positive ion mode. The precursor to product ion transitions monitored for VEN, ODV and Venlafaxine d6 were m/z 278.3→121.08, 264.2→107.1 and 284.4→121.0, respectively. The developed and validated method was used for the pharmacokinetic study of VEN in rats.
Keywords: Metabolite; O-desmethylvenlafaxine; UPLC–MS/ES; Venlafaxine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/ESI) method for simultaneous determination of venlafaxine and its three metabolites in human plasma.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007 May 1;850(1-2):405-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.12.019. Epub 2006 Dec 21. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17222591
-
Simultaneous stereoselective analysis of venlafaxine and O-desmethylvenlafaxine enantiomers in human plasma by HPLC-ESI/MS using a vancomycin chiral column.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007 May 1;850(1-2):183-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.11.021. Epub 2006 Nov 30. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17140867
-
Simultaneous quantification of venlafaxine and O-desmethylvenlafaxine in human plasma by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application in a pharmacokinetic study.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010 Mar 1;878(7-8):689-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.01.007. Epub 2010 Jan 18. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20133212
-
Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay for the simultaneous determination of venlafaxine and O-desmethylvenlafaxine in human plasma and its application to a bioequivalence study.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008 Jul 15;47(3):603-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2008.02.015. Epub 2008 Feb 26. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008. PMID: 18387768
-
Simultaneous determination of fluoxetine, venlafaxine, vortioxetine and their active metabolites in human plasma by LC-MS/MS using one-step sample preparation procedure.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Mar 20;181:113098. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113098. Epub 2020 Jan 11. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 31978643
Cited by
-
Revealing Pharmacokinetic Interactions of Tramadol, Tapentadol, and Venlafaxine: A Cutting-Edge Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analytical Approach in Rat Plasma.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025 Mar 19;8(4):1116-1128. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00722. eCollection 2025 Apr 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40242577
-
Multiple-reaction monitoring (MRM) LC-MS/MS quantitation of venlafaxine and its O-desmethyl metabolite for a preclinical pharmacokinetic study in rabbits.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 4;12(1):9322. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13389-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35661132 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of different electrodeposited NiCo2O4 microspheres anchored on a reduced graphene oxide platform: electrochemical sensor for anti-depressant drug venlafaxine.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 4;9(54):31609-31620. doi: 10.1039/c9ra04999a. eCollection 2019 Oct 1. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35527939 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modelling study of 4-hydroxyisoleucine using validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.RSC Adv. 2020 Feb 4;10(10):5525-5532. doi: 10.1039/c9ra08121f. eCollection 2020 Feb 4. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews J.M., Ninan P.T., Nemeroff C.B. Venlafaxine: a novel antidepressant that has a dual mechanism of action. Depression. 1996;4:48–56. - PubMed
-
- Hicks D.R., Wolaniuk D., Russell A. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of venlafaxine and O-desmethylvenlafaxine in biological fluids. Ther. Drug Monit. 1994;16:100–107. - PubMed
-
- Deecher D.C., Beyer C.E., Johnston G. Desvenlafaxine succinate: a new serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006;318:657–665. - PubMed
-
- Fogelman S.M., Schmider J., Venkatakrishnan K. O- and N-demethylation of venlafaxine in vitro by human liver microsomes and by microsomes from cDNA-transfected cells: effect of metabolic inhibitors and SSRI antidepressants. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;20:480–490. - PubMed
-
- Tzanakaki M., Guazzelli M., Nimatoudis I. Increased remission rates with venlafaxine compared with fluoxetine in hospitalized patients with major depression and melancholia. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2000;15:29–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

