A validated LC-MS/MS method for the determination of tolterodine and its metabolite in rat plasma and application to pharmacokinetic study
- PMID: 29403860
- PMCID: PMC5761003
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.04.005
A validated LC-MS/MS method for the determination of tolterodine and its metabolite in rat plasma and application to pharmacokinetic study
Abstract
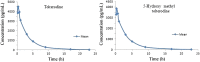
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method was used for simultaneous quantification of tolterodine and its metabolite 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine in rat plasma. Tolterodine-d6 and 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine-d14 were used as internal standards (IS). Chromatographic separation was performed on Ascentis Express RP amide (50 mm×4.6 mm, 2.7 μm) column with an isocratic mobile phase composed of 10 mM ammonium acetate and acetonitrile in the ratio of 20:80 (v/v), at a flow-rate of 0.5 mL/min. Tolterodine, tolterodine-d6, 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine and 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine-d14 were detected with proton adducts at m/z 326.1→147.1, 332.3→153.1, 342.2→223.1 and 356.2→223.1 in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) positive mode respectively. The drug, metabolite and internal standards were extracted by liquid-liquid extraction method. The method was validated over a linear concentration range of 20.00-5000.00 pg/mL for tolterodine and 20.00-5000.00 pg/mL for 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine. This method demonstrated intra- and inter-day precision of 0.62-6.36% and 1.73-4.84% for tolterodine, 1.38-4.22% and 1.62-4.25% for 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine respectively. This method also demonstrated intra- and inter-day accuracy of 98.75-103.56% and 99.20-104.40% for tolterodine, 98.08-104.67% and 98.73-103.06% for 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine respectively. Both analytes were found to be stable throughout freeze-thaw cycles, bench top and postoperative stability studies. This method was successfully applied for the pharmacokinetic analysis of rat plasma samples following i.v. administration.
Keywords: 5-Hydroxy methyl tolterodine; LC–MS/MS; Pharmacokinetics; Tolterodine.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Quantification of desloratadine in human plasma by LC-ESI-MS/MS and application to a pharmacokinetic study.J Pharm Anal. 2012 Jun;2(3):180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 31. J Pharm Anal. 2012. PMID: 29403740 Free PMC article.
-
Bioanalytical method development and validation of milnacipran in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS detection and its application to a pharmacokinetic study.J Pharm Anal. 2013 Dec;3(6):481-488. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.03.009. Epub 2013 Apr 29. J Pharm Anal. 2013. PMID: 29403859 Free PMC article.
-
Novel LC- ESI-MS/MS method for desvenlafaxine estimation human plasma: application to pharmacokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2016 Feb;30(2):249-55. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3542. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Biomed Chromatogr. 2016. PMID: 26095112
-
Simultaneous determination of tolterodine and its two metabolites, 5-hydroxymethyltolterodine and N-dealkyltolterodine in human plasma using LC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study.Arch Pharm Res. 2017 Nov;40(11):1287-1295. doi: 10.1007/s12272-017-0981-3. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Arch Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 29128914
-
Simultaneous determination of paclitaxel and lansoprazole in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS method and its application to a preclinical pharmacokinetic study of investigational PTX-LAN-PLGA nanoformulation.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019 Aug 15;1124:331-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.06.031. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31276955
Cited by
-
In Vitro Intestinal Permeability Studies and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Famotidine Microemulsion for Oral Delivery.Int Sch Res Notices. 2014 Dec 7;2014:452051. doi: 10.1155/2014/452051. eCollection 2014. Int Sch Res Notices. 2014. PMID: 27379272 Free PMC article.
-
HSPiP, Computational, and Thermodynamic Model-Based Optimized Solvents for Subcutaneous Delivery of Tolterodine Tartrate and GastroPlus-Based In Vivo Prediction in Humans: Part I.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 May 1;25(5):93. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02800-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38693316
-
HSPiP, Computational, and Thermodynamic Model-Based Optimized Solvents for Subcutaneous Delivery of Tolterodine Tartrate and GastroPlus‑Based In Vivo Prediction in Humans: Part II.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Jul 12;25(6):160. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02880-0. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38992299
References
-
- Pahlman I., Gozzi P. Serum protein binding of tolterodine and its major metabolites in humans and several animal species. Biopharm. Drug. Dispos. 1999;20(2):91–99. - PubMed
-
- Oishi M., Chiba K., Malhotra B. Effect of the CYP2D6⁎10 genotype on tolterodine pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010;38(9):1456–1463. - PubMed
-
- Elshafeey A.H., Kamel A.O., Fathallah M.M. Utility of nanosized microemulsion for transdermal delivery of tolterodine tartrate: ex-vivo permeation and in-vivo pharmacokinetic studies. Pharm. Res. 2009;26(11):2446–2453. - PubMed
-
- Nagabukuro H., Villa K.L., Wickham L.A. Comparative analysis of the effects of antimuscarinic agents on bladder functions in both nonhuman primates and rodents. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011;338(1):220–227. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

