LC-UV/MS quality analytics of paediatric artemether formulations
- PMID: 29403867
- PMCID: PMC5761056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.03.006
LC-UV/MS quality analytics of paediatric artemether formulations
Abstract
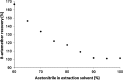
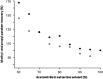
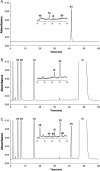
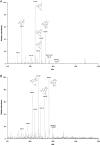
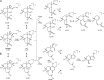
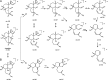
A highly selective and stability-indicating HPLC-method, combined with appropriate sample preparation steps, is developed for β-artemether assay and profiling of related impurities, including possible degradants, in a complex powder for oral suspension. Following HPLC conditions allowed the required selectivity: a Prevail organic acid (OA) column (250 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm), flow rate set at 1.5 mL/min combined with a linear gradient (where A=25 mM phosphate buffer (pH 2.5), and B=acetonitrile) from 30% to 75% B in a runtime of 60 min. Quantitative UV-detection was performed at 210 nm. Acetonitrile was applied as extraction solvent for sample preparation. Using acetonitrile-water mixtures as extraction solvent, a compartmental behaviour by a non-solving excipient-bound fraction and an artemether-solubilising free fraction of solvent was demonstrated, making a mobile phase based extraction not a good choice. Method validation showed that the developed HPLC-method is considered to be suitable for its intended regulatory stability-quality characterisation of β-artemether paediatric formulations. Furthermore, LC-MS on references as well as on stability samples was performed allowing identity confirmation of the β-artemether related impurities. MS-fragmentation scheme of β-artemether and its related substances is proposed, explaining the m/z values of the in-source fragments obtained.
Keywords: Artemisinin trioxane derivatives; MS-fragmentation; Paediatric formulations; Polar embedded organic acid column; Related impurities and degradation compounds; Sample preparation.
Figures


References
-
- Food & Drug Administration (FDA), Food and Drug Administration Amendments Act of 2007: Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act. FDA, Silver Spring, 2007.
-
- European Medicine Evaluation Agency (EMEA), EMEA/CHMP/PEG/194810/2005: Reflection paper: formulations of choice for the paediatric population; EMEA, London, 2006.
-
- Ceci A., Giaquinto C., Aboulker J.P. The task-force in Europe for drug development for the Young (TEDDY) network of excellence. Paediatr. Drugs. 2009;11:18–21. - PubMed
-
- Zajicek A. The national institutes of health and the best pharmaceuticals for children act. Paediatr. Drugs. 2009;11:45–47. - PubMed
-
- Connor E., Cure P. Creating hope and other incentives for drug development for children. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011;3(66):66cm1. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

