Quantitative and qualitative analysis of common peaks in chemical fingerprint of Yuanhu Zhitong tablet by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS
- PMID: 29403871
- PMCID: PMC5761090
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2013.12.004
Quantitative and qualitative analysis of common peaks in chemical fingerprint of Yuanhu Zhitong tablet by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS
Abstract
A quality control (QC) strategy for quantitative and qualitative analysis of "common peaks" in chemical fingerprint was proposed to analyze Yuanhu Zhitong tablet (YZT), using high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector and tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-MS/MS). The chromatographic separation was achieved on an Agilent Eclipse plus C18 column with a gradient elution using a mixture of 0.4‰ ammonium acetate aqueous (pH 6.0 adjusted with glacial acetic acid) and acetonitrile. In chemical fingerprint, 40 peaks were assigned as the "common peaks". For quantification of "common peaks", the detection wavelength was set at 254 nm, 270 nm, 280 nm and 345 nm, respectively. The method was validated and good results were obtained to simultaneously determine 10 analytes (protopine, jatrorrhizine, coptisine, palmatine, berberine, xanthotoxin, bergapten, tetrahydropalmatine, imperatorin and isoimperatorin). For qualification of "common peaks", 33 compounds including 10 quantitative analytes were identified or tentatively characterized using LC-MS/MS. These results demonstrated that the present approach may be a powerful and useful tool to tackle the complex quality issue of YZT.
Keywords: Alkaloids; Coumarins; HPLC-DAD–MS/MS; Quality control; Yuanhu Zhitong tablet.
Figures

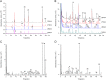

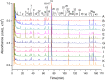

References
-
- Li S.P., Zhao J., Yang B. Strategies for quality control of Chinese medicines. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011;55(4):802–809. - PubMed
-
- Xu C.J., Liang Y.Z., Chau F.T. Pretreatments of chromatographic fingerprints for quality control of herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. A. 2006;1134(1–2):253–259. - PubMed
-
- Xu L., Han X., Qi Y. Multiple compounds determination and fingerprint analysis of Lidanpaishi tablet and keli by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2009;633(1):136–148. - PubMed
-
- Yang D.Z., An Y.Q., Jiang X.L. Development of a novel method combining HPLC fingerprint and multi-ingredients quantitative analysis for quality evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine preparation. Talanta. 2011;85(2):885–890. - PubMed
-
- Tang D., Yang D., Tang A. Simultaneous chemical fingerprint and quantitative analysis of Ginkgo biloba extract by HPLC-DAD. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010;396(8):3087–3095. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

