Stability-indicating assay method for determination of actarit, its process related impurities and degradation products: Insight into stability profile and degradation pathways☆
- PMID: 29403903
- PMCID: PMC5761480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2014.01.002
Stability-indicating assay method for determination of actarit, its process related impurities and degradation products: Insight into stability profile and degradation pathways☆
Abstract
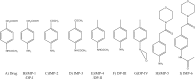
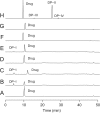
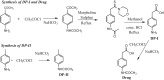
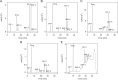
The stability of the drug actarit was studied under different stress conditions like hydrolysis (acid, alkaline and neutral), oxidation, photolysis and thermal degradation as recommended by International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines. Drug was found to be unstable in acidic, basic and photolytic conditions and produced a common degradation product while oxidative stress condition produced three additional degradation products. Drug was impassive to neutral hydrolysis, dry thermal and accelerated stability conditions. Degradation products were identified, isolated and characterized by different spectroscopic analyses. Drug and the degradation products were synthesized by a new route using green chemistry. The chromatographic separation of the drug and its impurities was achieved in a phenomenex luna C18 column employing a step gradient elution by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to photodiode array and mass spectrometry detectors (HPLC-PDA-MS). A specific and sensitive stability-indicating assay method for the simultaneous determination of the drug actarit, its process related impurities and degradation products was developed and validated.
Keywords: Actarit; Forced degradation; Stability-indicating assay method.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a novel stability-indicating HPLC method for the quantitative determination of eleven related substances in ezetimibe drug substance and drug product.Talanta. 2015 Jul 1;139:67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.02.039. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Talanta. 2015. PMID: 25882410
-
Stability-Indicating Method and LC-MS-MS Characterization of Forced Degradation Products of Sofosbuvir.J Chromatogr Sci. 2016 Oct 17;54(9):1631-1640. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmw119. J Chromatogr Sci. 2016. PMID: 27436268
-
A validated stability-indicating RP-HPLC method for levofloxacin in the presence of degradation products, its process related impurities and identification of oxidative degradant.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2009 Dec 5;50(5):710-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.05.038. Epub 2009 Jun 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2009. PMID: 19632800
-
Mini Review on Forced Degradation Studies on Anti-Epileptic Drugs and Beyond.J Chromatogr Sci. 2023 Jul 9;61(6):585-604. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmac070. J Chromatogr Sci. 2023. PMID: 35980304 Review.
-
Choices of chromatographic methods as stability indicating assays for pharmaceutical products: A review.Heliyon. 2021 Mar 27;7(3):e06553. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06553. eCollection 2021 Mar. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33855234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification, synthesis and characterization of process related impurities of benidipine hydrochloride, stress-testing/stability studies and HPLC/UPLC method validations.J Pharm Anal. 2015 Aug;5(4):256-268. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Feb 13. J Pharm Anal. 2015. PMID: 29403939 Free PMC article.
-
Chemometrics Approaches in Forced Degradation Studies of Pharmaceutical Drugs.Molecules. 2019 Oct 22;24(20):3804. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203804. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31652589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Validation of Carbonic Anhydrase II as the First Target of the Anti-Inflammatory Drug Actarit.Biomolecules. 2020 Nov 19;10(11):1570. doi: 10.3390/biom10111570. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33227945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujisawa H., Nishimura T., Inoue Y. Anti-inflammatory properties of the new antirheumatic agent 4-acetylaminophenylacetic acid. Arzneim.-Forsch. 1990;40:693–697. - PubMed
-
- Fujisawa H., Nishimura T., Motonaga A. Effect of actarit on type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Arzneim.-Forsch. 1994;44:64–68. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H., Fujisawa H., Abe C. Effect of Ms-932 Zˇ4-acetylaminophenylacetic acid on articular lesions in MRLrl mice. Int. J. Immunother. 1987;3:261–264.
-
- Nakagawa Y., Ogawa T., Kobayashi M. Immunopharmacological studies of 4 acetylamino phenylacetic acid (MS-932) Int. J. Immunother. 1990;6(3):131–140.
-
- Nakagawa Y., Ogawa T., Umezu K. Suppressive effect of 4-acetylaminophenylacetic acid (MS-932) on delayed-type hypersensitivity in mice. Int. J. Immunother. 1990;6:141–148.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

