Direct injection HILIC-MS/MS analysis of darunavir in rat plasma applying supported liquid extraction
- PMID: 29403914
- PMCID: PMC5761474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2014.05.001
Direct injection HILIC-MS/MS analysis of darunavir in rat plasma applying supported liquid extraction
Abstract
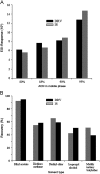
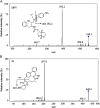
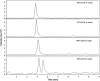
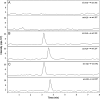
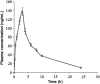
A novel bioanalytical method was developed and validated for the quantitative determination of darunavir (DRV) in rat plasma by employing hydrophilic interaction chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-MS/MS) with supported liquid extraction (SLE). Irbesartan (IRB) was used as an internal standard (IS). The analyte in rat plasma (200 µL) was isolated through SLE using ethyl acetate as the eluting solvent. The chromatographic separation was achieved on Luna-HILIC (250 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm) column with a mobile phase of 0.1% of formic acid in water:acetonitrile (5: 95, v/v), at a constant flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The MS/MS ion transitions for DRV (548.1→392.0) and IS (429.2→207.1) were monitored on an ion trap mass spectrometer, operating in the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. The lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) was 0.2 ng/mL and quantitation range was 0.2-5000 ng/mL. The method was validated for its selectivity, sensitivity, carryover, linearity, precision, accuracy, recovery, matrix effect and stability. The method was successfully applied to pharmacokinetic study in rats.
Keywords: Darunavir; HILIC–MS/MS; Rat plasma; Supported liquid extraction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of abacavir, tenofovir, darunavir, and raltegravir in human plasma and saliva using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015 Oct 10;114:390-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015. PMID: 26112927
-
A rapid LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of berberine and irbesartan in rat plasma: Application to the drug-drug pharmacokinetic interaction study after oral administration in rats.Biomed Chromatogr. 2021 Sep;35(9):e5144. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5144. Epub 2021 May 5. Biomed Chromatogr. 2021. PMID: 33880775
-
Development and Validation of High-Throughput Bioanalytical Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Method for the Quantification of Newly Synthesized Antitumor Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors in Human Plasma.Molecules. 2020 Dec 6;25(23):5753. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235753. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33291270 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of lipoic acid in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS with electrospray ionization: assay development, validation and application to a pharamcokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2004 Nov;18(9):681-6. doi: 10.1002/bmc.375. Biomed Chromatogr. 2004. PMID: 15386498
-
Application of a validated ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of darunavir in human plasma for a bioequivalence study in Indian subjects.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011 Aug 15;879(24):2443-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 18. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21788160
Cited by
-
Development and Validation of a Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Asparagine in Human Serum.Int J Anal Chem. 2020 Feb 28;2020:6980392. doi: 10.1155/2020/6980392. eCollection 2020. Int J Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32180807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alpert A.J. Hydrophilic-interaction chromatography for the separation of peptides, nucleic acids and other polar compounds. J. Chromatogr. A. 1990;499:177–196. - PubMed
-
- Song Q., Naidong W. Analysis of omeprazole and 5-OH omeprazole in human plasma using hydrophilic interaction chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC–MS/MS) – eliminating evaporation and reconstitution steps in 96-well liquid/liquid extraction. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2006;830:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh Y. Potential of HILIC–MS in quantitative bioanalysis of drugs and drug metabolites. J. Sep. Sci. 2008;31:1481–1491. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen H.P., Schug K.A. The advantages of ESI-MS detection in conjunction with HILIC mode separations: fundamentals and applications. J. Sep. Sci. 2008;31:1465–1480. - PubMed
-
- Baughman T.M., Wright W.L., Hutton K.A. Determination of zanamivir in rat and monkey plasma by positive ion hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC)–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007;852:505–511. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

