A newfangled study using risk silhouette and uncertainty approximation for quantification of acyclovir in diverse formulation
- PMID: 29403916
- PMCID: PMC5761472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2014.05.005
A newfangled study using risk silhouette and uncertainty approximation for quantification of acyclovir in diverse formulation
Abstract
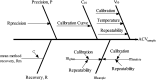
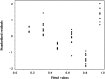
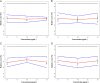
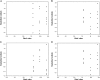
Risk assessment and uncertainty approximation are two major and important parameters that need to be adopted for the development of pharmaceutical process to ensure reliable results. Additionally, there is a need to switch from the traditional method validation checklist to provide a high level of assurance of method reliability to measure quality attribute of a drug product. In the present work, evaluation of risk profile, combined standard uncertainty and expanded uncertainty in the analysis of acyclovir were studied. Uncertainty was calculated using cause-effect approach, and to make it more accurately applicable a method was validated in our laboratory as per the ICH guidelines. While assessing the results of validation, the calibration model was justified by the lack of fit and Levene׳s test. Risk profile represents the future applications of this method. In uncertainty the major contribution is due to sample concentration and mass. This work demonstrates the application of theoretical concepts of calibration model tests, relative bias, risk profile and uncertainty in routine methods used for analysis in pharmaceutical field.
Keywords: Acyclovir; Combined standard uncertainty; Expanded uncertainty; Relative bias; Risk profile.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Derivation of uncertainty functions from validation studies in biological fluids: application to the analysis of caffeine and its major metabolites in human plasma samples.J Chromatogr A. 2014 Aug 1;1353:121-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.047. Epub 2014 May 27. J Chromatogr A. 2014. PMID: 24925447
-
Comparison of the quantitative performances and measurement uncertainty estimates obtained during method validation versus routine applications of a novel hydrophilic interaction chromatography method for the determination of cidofovir in human plasma.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012 Jan 5;57:153-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.08.040. Epub 2011 Sep 10. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012. PMID: 21959349
-
Simultaneous quantification of five bioactive phenylethanoid, iridoid, and flavonol glycosides in Duranta erecta L.: Ultra performance liquid chromatography method validation and uncertainty measurement.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Sep 10;174:711-717. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.06.044. Epub 2019 Jul 1. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 31288194
-
Bias in analytical chemistry: A review of selected procedures for incorporating uncorrected bias into the expanded uncertainty of analytical measurements and a graphical method for evaluating the concordance of reference and test procedures.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Aug;495:129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.03.1633. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30935874 Review.
-
Risk management frameworks for human health and environmental risks.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003 Nov-Dec;6(6):569-720. doi: 10.1080/10937400390208608. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003. PMID: 14698953 Review.
References
-
- International Organisation for Standardization, ISO-IEC 17025:1999: General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibrating Laboratories, ISO, Geneva, 1999.
-
- Elisavet A., Eleni T., Lazaros T. Uncertainty in spectrophotometric analysis – “error propagation break up”, a novel statistical method for uncertainty management. Talanta. 2011;85:2385–2390. - PubMed
-
- Eurachem Guide: Quantifying Uncertainty in Analytical Measurement, Laboratory of the Government Chemist, London, 2012 (isbn:978-0-948926-30-3).
-
- International Conference on Harmonization, Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology, Consensus Guidelines, ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guidelines, 1996.
-
- International Conference on Harmonization, Q2A Validation of Analytical Procedures: Consensus Guidelines, ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guidelines, 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

