High-sensitivity simultaneous liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel in human plasma
- PMID: 29403945
- PMCID: PMC5762240
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2015.02.002
High-sensitivity simultaneous liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel in human plasma
Abstract
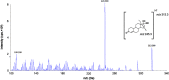
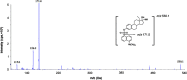
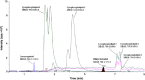
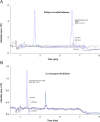
A sensitive and simultaneous liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method was developed and validated for quantification of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel. The analytes were extracted with methyl-tert-butyl ether: n-hexane (50:50, v/v) solvent mixture, followed by dansyl derivatization. The chromatographic separation was performed on a Kinetex C18 (50 mm×4.6 mm, 2.6 µm) column with a mobile phase of 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in water and acetonitrile in gradient composition. The mass transitions were monitored in electrospray positive ionization mode. The assay exhibited a linear range of 0.100-20.0 ng/mL for levonorgestrel and 4.00-500 pg/mL for ethinyl estradiol in human plasma. A run time of 9.0 min for each sample made it possible to analyze a throughput of more than 100 samples per day. The validated method has been successfully used to analyze human plasma samples for application in pharmacokinetic and bioequivalence studies.
Keywords: Derivatization; Ethinyl estradiol; Human plasma; LC–MS/MS; Levonorgestrel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of Ethinyl Estradiol and Levonorgestrel in Human Plasma with Prednisone as Internal Standard Using Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019 Jul-Sep;11(3):254-261. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_68_19. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019. PMID: 31555032 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a high-sensitivity liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) method with chemical derivatization for the determination of ethinyl estradiol in human plasma.Biomed Chromatogr. 2004 Sep;18(7):414-21. doi: 10.1002/bmc.329. Biomed Chromatogr. 2004. PMID: 15340965
-
Simultaneous determination of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol in human plasma by high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry--experiences on developing a highly selective method using derivatization reagent for enhancing sensitivity.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005 Oct 25;825(2):223-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.01.012. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 16213451
-
Quantitative high-throughput determination of endogenous retinoids in human plasma using triple-stage liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2007;21(7):1176-86. doi: 10.1002/rcm.2946. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2007. PMID: 17330217
-
Selective and rapid liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay of dutasteride in human plasma.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004 Sep 25;809(1):117-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.06.010. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15282101
Cited by
-
Comparison of ESI- and APCI-LC-MS/MS methods: A case study of levonorgestrel in human plasma.J Pharm Anal. 2016 Dec;6(6):356-362. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 29. J Pharm Anal. 2016. PMID: 29404004 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Ethinyl Estradiol and Levonorgestrel in Human Plasma with Prednisone as Internal Standard Using Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019 Jul-Sep;11(3):254-261. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_68_19. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019. PMID: 31555032 Free PMC article.
-
A sensitive and robust UPLC-MS/MS method for quantitation of estrogens and progestogens in human serum.Contraception. 2019 Apr;99(4):244-250. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.12.010. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Contraception. 2019. PMID: 30685285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levonorgestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol Information. Available from: 〈http://www.drugs.com/cdi/levonorgestrel-ethinyl-estradiol.html〉 (accessed 09/02/2014).
-
- Lutera Drug Product Information. Available from: 〈http://www.rxlist.com/lutera-drug/clinical-pharmacology.htm〉 (accessed 09/02/2014).
-
- Shou W.Z., Jiang X., Naidong W. Development and validation of a high-sensitivity liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) method with chemical derivatization for the determination of ethinyl estradiol in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004;18:414–421. - PubMed
-
- Wheaton J.P., Chambers E.E., Fountain K.J. Challenges in developing an ultra-sensitive bioanalytical method for ethinylestradiol in human plasma. Bioanalysis. 2012;4:769–781. - PubMed
-
- Matějíček D., Kubáň V. High performance liquid chromatography/ion-trap mass spectrometry for separation and simultaneous determination of ethynylestradiol, gestodene, levonorgestrel, cyproterone acetate and desogestrel. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2007;588:304–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

