Optimization, validation and application of an assay for the activity of HMG-CoA reductase in vitro by LC-MS/MS
- PMID: 29403953
- PMCID: PMC5762244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2015.06.002
Optimization, validation and application of an assay for the activity of HMG-CoA reductase in vitro by LC-MS/MS
Abstract
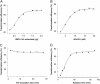
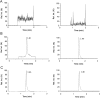
A stable HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) reaction in vitro was developed by a sensitive, selective and precise liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method. The optimized enzyme reaction condition contained 1.5 μg of HMGR, 20 nM of NADPH with 50 min of reaction time. The method was validated by several intra- and inter-day assays. The production transitions of m/z 147.0/59.1 and m/z 154.0/59.1 were used to detect and quantify mevalonolactone (MVAL) and MVAL-D7, respectively. The accuracy and precision of the method were evaluated over the concentration range of 0.005-1.000 μg/mL for MVAL and 0.010-0.500 μg/mL for lovastatin acid in three validation batch runs. The lower limit of quantitation was found to be 0.005 μg/mL for MVAL and 0.010 μg/mL for lovastatin acid. Intra-day and inter-day precision ranged from 0.95% to 2.39% and 2.26% to 3.38% for MVAL, 1.46% to 3.89% and 0.57% to 5.10% for lovastatin acid, respectively. The results showed that the active ingredients in Xuezhikang capsules were 12.2 and 14.5 mg/g, respectively. This assay method could be successfully applied to the quality control study of Xuezhikang capsule for the first time.
Keywords: HMG-CoA reductase; LC–MS/MS; Mevalonolactone; Quality control; Xuezhikang.
Figures
References
-
- Zetterström R. The 1964 Nobel Prize for the discovery of the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Acta Paediatr. 2009;98:1223–1227. - PubMed
-
- Waterham H.R. Defects of cholesterol biosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:5442–5449. - PubMed
-
- Istvan E.S., Deisenhofer J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001;292:1160–1164. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

