Simultaneous analysis of allopurinol and oxypurinol using a validated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method in human plasma
- PMID: 29404018
- PMCID: PMC5686867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2016.05.005
Simultaneous analysis of allopurinol and oxypurinol using a validated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method in human plasma
Abstract
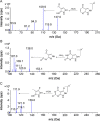
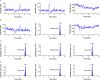
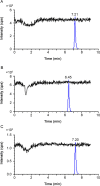
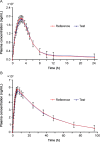
The present study describes a simple, reliable and reproducible liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method (LC-MS/MS) for the simultaneous determination of allopurinol and its active metabolite, oxypurinol in human plasma for a pharmacokinetic/bioequivalence study. After protein precipitation (PPT) of 100 µL plasma sample with 1.0% formic acid in acetonitrile, the recovery of the analytes and allopurinol-d2 as an internal standard ranged from 85.36% to 91.20%. The analytes were separated on Hypersil Gold (150 mm×4.6 mm, 5 µm) column using 0.1% formic acid-acetonitrile (98:2, v/v) as the mobile phase. Quantification was done using electrospray ionization in the positive mode. The calibration concentration range was established from 60.0 to 6000 ng/mL for allopurinol and 80.0-8000 ng/mL for oxypurinol. Matrix effect in human plasma, expressed as IS-normalized matrix factors ranged from 1.003 to 1.030 for both the analytes. The developed method was found suitable for a clinical study with 300 mg allopurinol tablet formulation in healthy subjects.
Keywords: Allopurinol; Bioequivalence study; Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry; Oxypurinol.
Figures
References
-
- Day R.O., Graham G.G., Hicks M. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of allopurinol and oxypurinol. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007;46:623–644. - PubMed
-
- Breithaupt H., Tittel M. Kinetics of allopurinol after single intravenous and oral doses. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1982;22:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Simmonds H.A. Urinary excretion of purines, pyrimidines and pyrazolopyrimidines in patients treated with allopurinol or oxypurinol. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1969;23:353–364. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

