Novel NAC-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide acid) nanoparticles for cataract treatment: preparation, characterization, evaluation of structure, cytotoxicity, and molecular docking studies
- PMID: 29404207
- PMCID: PMC5796282
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4270
Novel NAC-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide acid) nanoparticles for cataract treatment: preparation, characterization, evaluation of structure, cytotoxicity, and molecular docking studies
Abstract
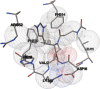
Background: N-acetylcarnosine (NAC), a dipeptide with powerful antioxidant properties that is extensively used as a pharmaceutical prodrug for the treatment of cataract and acute gastric disease, was investigated by molecular dynamics with the GROMACS program in order to understand the solvent effect on peptide conformation of the peptide molecule used as a component of a drug and which presents substantial information on where drug molecules bind and how they exert their effects. Besides, molecular docking simulation was performed by using the AutoDock Vina program which identify the kind of interaction between the drug and proteins. A delivery system based on poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles (NPs) loaded with NAC (NAC-PLGA-NPs) for the treatment of cataract was prepared for the first time in this study in order to enhance drug bioavailability and biocompatibility. The objective of this work was to prepare and evaluate the structural formulation, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies of NAC-loaded NPs based on PLGA for cataract treatment.
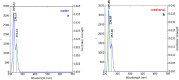
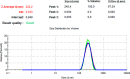
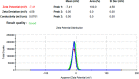
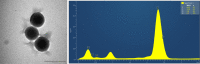
Methods: PLGA and NAC-loaded PLGA NPs were prepared using the double emulsion (w/o/w) method, and characterizations of the NPs were carried out with UV-Vis spectrometer to determine drug concentration, the Zeta-sizer system to analyze size and zeta potential, FTIR spectrometer to determine the incorporation of drug and PLGA, and TEM analysis for morphological evaluation.
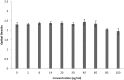
Results: NAC-loaded PLGA NPs were successfully obtained according to UV-Vis and FTIR spectroscopy, Zeta-sizer system. And it was clearly observed from the TEM analysis that the peptide-loaded NPs had spherical and non-aggregated morphology. Also, the NPs had low toxicity at lower concentrations, and toxicity was augmented by increasing the concentration of the drug.
Discussion: The NAC molecule, which has been investigated as a drug molecule due to its antioxidant and oxidative stress-reducing properties, especially in cataract treatment, was encapsulated with a PLGA polymer in order to increase drug bioavailability. This study may contribute to the design of drugs for cataract treatment with better reactivity and stability.
Keywords: FTIR; GROMACS; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamic; NAC; Nanoparticle; PLGA; TEM; Zeta-sizer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures














Similar articles
-
Computational design of Phe-Tyr dipeptide and preparation, characterization, cytotoxicity studies of Phe-Tyr dipeptide loaded PLGA nanoparticles for the treatment of hypertension.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018 Aug;36(11):2893-2907. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2017.1371644. Epub 2017 Sep 11. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018. PMID: 28835169
-
Molecular docking of immunogenic peptide of Toxoplasma gondii and encapsulation with polymer as vaccine candidate.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):744-754. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1469024. Epub 2018 May 9. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29741393
-
Effect of Solvents, Stabilizers and the Concentration of Stabilizers on the Physical Properties of Poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles: Encapsulation, In Vitro Release of Indomethacin and Cytotoxicity against HepG2-Cell.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 15;14(4):870. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040870. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456705 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the formulation of PLGA microparticles for controlled drug delivery.Prog Biomater. 2020 Dec;9(4):153-174. doi: 10.1007/s40204-020-00139-y. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Prog Biomater. 2020. PMID: 33058072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Design of Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Nanocarriers for Medical Applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 11;8:48. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00048. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32117928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Controlled release of carnosine from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) beads using nanomechanical magnetic trigger towards the treatment of glioblastoma.Nanoscale Adv. 2022 Apr 27;4(10):2242-2249. doi: 10.1039/d2na00032f. eCollection 2022 May 17. Nanoscale Adv. 2022. PMID: 36133698 Free PMC article.
-
Laurus nobilis L. Essential Oil-Loaded PLGA as a Nanoformulation Candidate for Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2022 Mar 15;27(6):1899. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061899. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335262 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation potential of N-Acetylcysteine loaded PLGA nanoparticles for the management of tuberculosis: In vitro lung deposition and efficacy studies.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Jan 18;3:100084. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100084. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35112077 Free PMC article.
-
Niosomes loading N-acetyl-L-cysteine for cancer treatment in vivo study.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;397(6):4339-4353. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02893-9. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38091079
-
An approach to revolutionize cataract treatment by enhancing drug probing through intraocular cell line.Libyan J Med. 2018 Dec;13(1):1500347. doi: 10.1080/19932820.2018.1500347. Libyan J Med. 2018. PMID: 30045674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babizhayev MA. Failure to withstand oxidative stress induced by phospholipid hydroperoxides as a possible cause of the lens opacities in systemic diseases and ageing. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—Molecular Basis of Disease. 1996;1315(2):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(95)00091-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babizhayev MA, Deyev AI, Yermakova VN, Semiletov YA, Davydova NG, Kurysheva NI, Zhukotskii AV, Goldman IM. N-acetylcarnosine, a natural histidine-containing dipeptide, as a potent ophthalmic drug in treatment of human cataracts. Peptides. 2001;22(6):979–994. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00407-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berendsen HJ, Postma JV, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola A, Haak J. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. Journal of Chemical Physics. 1984;81(8):3684–3690. doi: 10.1063/1.448118. - DOI
-
- Brannon-Peppas L. Recent advances on the use of biodegradable microparticles and nanoparticles in controlled drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 1995;116(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(94)00324-x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

