Gene-based association study for lipid traits in diverse cohorts implicates BACE1 and SIDT2 regulation in triglyceride levels
- PMID: 29404214
- PMCID: PMC5793713
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4314
Gene-based association study for lipid traits in diverse cohorts implicates BACE1 and SIDT2 regulation in triglyceride levels
Abstract
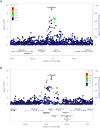
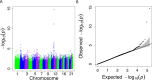
Plasma lipid levels are risk factors for cardiovascular disease, a leading cause of death worldwide. While many studies have been conducted on lipid genetics, they mainly focus on Europeans and thus their transferability to diverse populations is unclear. We performed SNP- and gene-level genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of four lipid traits in cohorts from Nigeria and the Philippines and compared them to the results of larger, predominantly European meta-analyses. Two previously implicated loci met genome-wide significance in our SNP-level GWAS in the Nigerian cohort, rs34065661 in CETP associated with HDL cholesterol (P = 9.0 × 10-10) and rs1065853 upstream of APOE associated with LDL cholesterol (P = 6.6 × 10-9). The top SNP in the Filipino cohort associated with triglyceride levels (rs662799; P = 2.7 × 10-16) and has been previously implicated in other East Asian studies. While this SNP is located directly upstream of well known APOA5, we show it may also be involved in the regulation of BACE1 and SIDT2. Our gene-based association analysis, PrediXcan, revealed decreased expression of BACE1 and decreased expression of SIDT2 in several tissues, all driven by rs662799, significantly associate with increased triglyceride levels in Filipinos (FDR <0.1). In addition, our PrediXcan analysis implicated gene regulation as the mechanism underlying the associations of many other previously discovered lipid loci. Our novel BACE1 and SIDT2 findings were confirmed using summary statistics from the Global Lipids Genetic Consortium (GLGC) meta-GWAS.
Keywords: GWAS; Gene expression; Lipids; Population genetics; PrediXcan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genetically regulated gene expression underlies lipid traits in Hispanic cohorts.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 8;14(8):e0220827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220827. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31393916 Free PMC article.
-
Association of genetic variants influencing lipid levels with coronary artery disease in Japanese individuals.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046385. Epub 2012 Sep 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23050023 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association with lipids in Filipinos: waist circumference modifies an APOA5 effect on triglyceride levels.J Lipid Res. 2013 Nov;54(11):3198-205. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P042077. Epub 2013 Sep 10. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 24023260 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic regulation of adipose tissue transcript expression is involved in modulating serum triglyceride and HDL-cholesterol.Gene. 2017 Oct 20;632:50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.08.019. Epub 2017 Aug 26. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28844666 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of gene-by-sex interactions for lipid traits in diverse populations from the population architecture using genomics and epidemiology study.BMC Genet. 2013 May 1;14:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-33. BMC Genet. 2013. PMID: 23634756 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into double-stranded RNA recognition and transport by SID-1.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jul;31(7):1095-1104. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01276-9. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38664565
-
The Variant rs1784042 of the SIDT2 Gene is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome through Low HDL-c Levels in a Mexican Population.Genes (Basel). 2020 Oct 14;11(10):1192. doi: 10.3390/genes11101192. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066450 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between SIDT2 and ABCA1 Variants with Nutrients on HDL-c Levels in Mexican Adults.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 11;15(2):370. doi: 10.3390/nu15020370. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678241 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of sub-Saharan African studies provides insights into genetic architecture of lipid traits.Nat Commun. 2022 May 11;13(1):2578. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30098-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35546142 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically regulated gene expression underlies lipid traits in Hispanic cohorts.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 8;14(8):e0220827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220827. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31393916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardlie KG, Deluca DS, Segrè AV, Sullivan TJ, Young TR, Gelfand ET, Trowbridge CA, Maller JB, Tukiainen T, Lek M, Ward LD, Kheradpour P, Iriarte B, Meng Y, Palmer CD, Esko T, Winckler W, Hirschhorn JN, Kellis M, MacArthur DG, Getz G, Shabalin AA, Li G, Zhou Y-H, Nobel AB, Rusyn I, Wright FA, Lappalainen T, Ferreira PG, Ongen H, Rivas MA, Battle A, Mostafavi S, Monlong J, Sammeth M, Mele M, Reverter F, Goldmann JM, Koller D, Guigó R, McCarthy MI, Dermitzakis ET, Gamazon ER, Im HK, Konkashbaev A, Nicolae DL, Cox NJ, Flutre T, Wen X, Stephens M, Pritchard JK, Tu Z, Zhang B, Huang T, Long Q, Lin L, Yang J, Zhu J, Liu J, Brown A, Mestichelli B, Tidwell D, Lo E, Salvatore M, Shad S, Thomas JA, Lonsdale JT, Moser MT, Gillard BM, Karasik E, Ramsey K, Choi C, Foster BA, Syron J, Fleming J, Magazine H, Hasz R, Walters GD, Bridge JP, Miklos M, Sullivan S, Barker LK, Traino HM, Mosavel M, Siminoff LA, Valley DR, Rohrer DC, Jewell SD, Branton PA, Sobin LH, Barcus M, Qi L, McLean J, Hariharan P, Um KS, Wu S, Tabor D, Shive C, Smith AM, Buia SA, Undale AH, Robinson KL, Roche N, Valentino KM, Britton A, Burges R, Bradbury D, Hambright KW, Seleski J, Korzeniewski GE, Erickson K, Marcus Y, Tejada J, Taherian M, Lu C, Basile M, Mash DC, Volpi S, Struewing JP, Temple GF, Boyer J, Colantuoni D, Little R, Koester S, Carithers LJ, Moore HM, Guan P, Compton C, Sawyer SJ, Demchok JP, Vaught JB, Rabiner CA, Lockhart NC, Ardlie KG, Getz G, Wright FA, Kellis M, Volpi S, Dermitzakis ET. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science. 2015;348(6235):648–660. doi: 10.1126/science.1262110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asselbergs FW, Guo Y, Van Iperen EP, Sivapalaratnam S, Tragante V, Lanktree MB, Lange LA, Almoguera B, Appelman YE, Barnard J, Baumert J, Beitelshees AL, Bhangale TR, Chen YDI, Gaunt TR, Gong Y, Hopewell JC, Johnson T, Kleber ME, Langaee TY, Li M, Li YR, Liu K, McDonough CW, Meijs MF, Middelberg RP, Musunuru K, Nelson CP, O’Connell JR, Padmanabhan S, Pankow JS, Pankratz N, Rafelt S, Rajagopalan R, Romaine SP, Schork NJ, Shaffer J, Shen H, Smith EN, Tischfield SE, Van Der Most PJ, Van Vliet-Ostaptchouk JV, Verweij N, Volcik KA, Zhang L, Bailey KR, Bailey KM, Bauer F, Boer JM, Braund PS, Burt A, Burton PR, Buxbaum SG, Chen W, Cooper-Dehoff RM, Cupples LA, Dejong JS, Delles C, Duggan D, Fornage M, Furlong CE, Glazer N, Gums JG, Hastie C, Holmes MV, Illig T, Kirkland SA, Kivimaki M, Klein R, Klein BE, Kooperberg C, Kottke-Marchant K, Kumari M, Lacroix AZ, Mallela L, Murugesan G, Ordovas J, Ouwehand WH, Post WS, Saxena R, Scharnagl H, Schreiner PJ, Shah T, Shields DC, Shimbo D, Srinivasan SR, Stolk RP, Swerdlow DI, Taylor HA, Topol EJ, Toskala E, Van Pelt JL, Van Setten J, Yusuf S, Whittaker JC, Zwinderman AH, Anand SS, Balmforth AJ, Berenson GS, Bezzina CR, Boehm BO, Boerwinkle E, Casas JP, Caulfield MJ, Clarke R, Connell JM, Cruickshanks KJ, Davidson KW, Day IN, De Bakker PI, Doevendans PA, Dominiczak AF, Hall AS, Hartman CA, Hengstenberg C, Hillege HL, Hofker MH, Humphries SE, Jarvik GP, Johnson JA, Kaess BM, Kathiresan S, Koenig W, Lawlor DA, März W, Melander O, Mitchell BD, Montgomery GW, Munroe PB, Murray SS, Newhouse SJ, Onland-Moret NC, Poulter N, Psaty B, Redline S, Rich SS, Rotter JI, Schunkert H, Sever P, Shuldiner AR, Silverstein RL, Stanton A, Thorand B, Trip MD, Tsai MY, Van Der Harst P, Van Der Schoot E, Van Der Schouw YT, Verschuren WM, Watkins H, Wilde AA, Wolffenbuttel BH, Whitfield JB, Hovingh GK, Ballantyne CM, Wijmenga C, Reilly MP, Martin NG, Wilson JG, Rader DJ, Samani NJ, Reiner AP, Hegele RA, Kastelein JJ, Hingorani AD, Talmud PJ, Hakonarson H, Elbers CC, Keating BJ, Drenos F. Large-scale gene-centric meta-analysis across 32 studies identifies multiple lipid loci. American Journal of Human Genetics. 2012;91(5):823–838. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.08.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

