Electrical Stimulation Modulates High γ Activity and Human Memory Performance
- PMID: 29404403
- PMCID: PMC5797477
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0369-17.2018
Electrical Stimulation Modulates High γ Activity and Human Memory Performance
Abstract
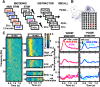
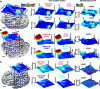
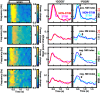
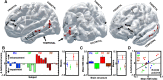
Direct electrical stimulation of the brain has emerged as a powerful treatment for multiple neurological diseases, and as a potential technique to enhance human cognition. Despite its application in a range of brain disorders, it remains unclear how stimulation of discrete brain areas affects memory performance and the underlying electrophysiological activities. Here, we investigated the effect of direct electrical stimulation in four brain regions known to support declarative memory: hippocampus (HP), parahippocampal region (PH) neocortex, prefrontal cortex (PF), and lateral temporal cortex (TC). Intracranial EEG recordings with stimulation were collected from 22 patients during performance of verbal memory tasks. We found that high γ (62-118 Hz) activity induced by word presentation was modulated by electrical stimulation. This modulatory effect was greatest for trials with "poor" memory encoding. The high γ modulation correlated with the behavioral effect of stimulation in a given brain region: it was negative, i.e., the induced high γ activity was decreased, in the regions where stimulation decreased memory performance, and positive in the lateral TC where memory enhancement was observed. Our results suggest that the effect of electrical stimulation on high γ activity induced by word presentation may be a useful biomarker for mapping memory networks and guiding therapeutic brain stimulation.
Keywords: ECoG; brain stimulation; cognitive enhancement; high-frequency oscillations; intracranial EEG; γ-activity.
Figures


References
-
- Bickford RG, Mulder DW, Dodge HW, Svien HJ, Rome HP (1958) Changes in memory function produced by electrical stimulation of the temporal lobe in man. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis 36:227–240; discussion 241–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
