An Optimized Synthetic-Bioinformatic Natural Product Antibiotic Sterilizes Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-Infected Wounds
- PMID: 29404414
- PMCID: PMC5784245
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00528-17
An Optimized Synthetic-Bioinformatic Natural Product Antibiotic Sterilizes Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-Infected Wounds
Abstract
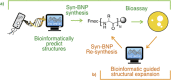
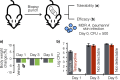
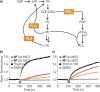
The antibiotic paenimucillin A was originally identified using a culture-independent synthetic-bioinformatic natural product (syn-BNP) discovery approach. Here we report on a bioinformatics-guided survey of paenimucillin A analogs that led to the discovery of paenimucillin C. Paenimucillin C inhibits the growth of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates, as well as other Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. In a rat cutaneous wound model, it completely sterilized MDR A. baumannii wound infections with no sign of rebound. Mechanistic studies point to a membrane-associated mode of action that results in leakage of intracellular contents. IMPORTANCE Natural product-inspired antibiotics have saved millions of lives and played a critical role in modern medicine. However, the emergence of drug-resistant pathogens is outpacing the rate at which new clinically useful antibiotics are being discovered. The lack of a means to combat infections caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) Acinetobacter baumannii is of particular concern. The sharp increase in cases of MDR A. baumannii infections in recent years prompted the CDC (https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest_threats.html) and WHO (http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/global-priority-list-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria/en/) to list this pathogen as a "serious threat" and "critical pathogen," respectively. Here we report a new antibiotic, paenimucillin C, active against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens, including many clinical isolates of MDR A. baumannii strains. Mechanistic studies point to membrane disruption leading to leakage of intracellular contents as its antibacterial mode of action. Paenimucillin C sterilizes MDR A. baumannii infections in a rat cutaneous wound model with no sign of rebound infection, providing a potential new therapeutic regimen.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; antibiotics; syn-BNP; wound infections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fluorescence-Based Detection of Natural Transformation in Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.J Bacteriol. 2018 Sep 10;200(19):e00181-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00181-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30012729 Free PMC article.
-
Global Assessment of the Activity of Tigecycline against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens between 2004 and 2014 as Part of the Tigecycline Evaluation and Surveillance Trial.mSphere. 2017 Jan 18;2(1):e00310-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00310-16. eCollection 2017 Jan-Feb. mSphere. 2017. PMID: 28124025 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii in Europe: clinical impact and therapeutic options.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012 Feb;39(2):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.10.004. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012. PMID: 22113193 Review.
-
Highly Synergistic Effects of Melittin with Conventional Antibiotics Against Multidrug-Resistant Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microb Drug Resist. 2019 Mar;25(2):193-202. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0016. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Microb Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 30281385
-
Treatment of Acinetobacter infections.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010 Apr;11(5):779-88. doi: 10.1517/14656561003596350. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20210684 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Large-Scale Genome Mining and Candidate Prioritization for Natural Product Discovery.Mar Drugs. 2022 Jun 16;20(6):398. doi: 10.3390/md20060398. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35736201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive Synthetic-Bioinformatic Natural Product Cyclic Peptides Inspired by Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Gene Clusters from the Human Microbiome.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Oct 9;141(40):15737-15741. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b07317. Epub 2019 Sep 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31545899 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Metabologenomics Analysis of Polar Actinomycetes.Mar Drugs. 2021 Feb 10;19(2):103. doi: 10.3390/md19020103. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33578887 Free PMC article.
-
Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 23;12(1):3864. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24133-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34162873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure Prediction and Synthesis of Pyridine-Based Macrocyclic Peptide Natural Products.Org Lett. 2021 Jan 15;23(2):253-256. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c02699. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Org Lett. 2021. PMID: 32845158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2017. Biggest threats: antibiotic/antimicrobial resistance. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest_threats.html. Accessed December 2017.
-
- Tacconelli E, Magrini N. 2017. Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland: http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/global-priority-list-antibioti....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

