Gut Microbiota Offers Universal Biomarkers across Ethnicity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Diagnosis and Infliximab Response Prediction
- PMID: 29404425
- PMCID: PMC5790872
- DOI: 10.1128/mSystems.00188-17
Gut Microbiota Offers Universal Biomarkers across Ethnicity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Diagnosis and Infliximab Response Prediction
Abstract
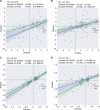
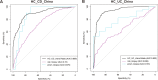
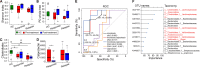
Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the onset and perpetuation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Given that gut microbiotas vary across geography and ethnicity, it remains obscure whether any universal microbial signatures for IBD diagnosis and prognosis evaluation exist irrespective of populations. Here we profiled the fecal microbiota of a series of Chinese IBD patients and combined them with two Western IBD cohorts, PRISM and RISK, for meta-analyses. We found that the gut microbial alteration patterns in IBD are similar among Chinese and Westerners. Our prediction model based on gut microbiome for IBD diagnosis is robust across the cohorts, which showed 87.5% and 79.1% prediction accuracy in Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) patients, respectively. A relative increase in the levels of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria (Enterobacteriaceae) and a relative decrease in the levels of Firmicutes (Clostridiales) were strongly correlated with IBD severity (P < 0.05). Additionally, restoration of gut microbiota diversity and a significant increase in Clostridiales relative abundance were found in patients responding to infliximab (IFX [Remicade]) treatment compared to those in relapse. Moreover, certain microbes, mainly Clostridiales, predicted the treatment effectiveness with 86.5% accuracy alone and 93.8% accuracy in combination with calprotectin levels and Crohn's disease activity index (CDAI). Taking the results together, we conclude that gut microbiota can offer a set of universal biomarkers for diagnosis, disease activity evaluation, and infliximab treatment response prediction in IBD. IMPORTANCE In the present report, we show that the human fecal microbiota contains promising and universal biomarkers for the noninvasive evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease severity and IFX treatment efficacy, emphasizing the potential ability to mine the gut microbiota as a modality to stratify IBD patients and apply personalized therapy for optimal outcomes.
Keywords: disease activity; gut microbiota; inflammatory bowel disease; infliximab treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Ng SC, Tang W, Leong RW, Chen M, Ko Y, Studd C, Niewiadomski O, Bell S, Kamm MA, de Silva HJ, Kasturiratne A, Senanayake YU, Ooi CJ, Ling KL, Ong D, Goh KL, Hilmi I, Ouyang Q, Wang YF, Hu P, Zhu Z, Zeng Z, Wu K, Wang X, Xia B, Li J, Pisespongsa P, Manatsathit S, Aniwan S, Simadibrata M, Abdullah M, Tsang SW, Wong TC, Hui AJ, Chow CM, Yu HH, Li MF, Ng KK, Ching J, Wu JC, Chan FK, Sung JJ; Asia-Pacific Crohn's and Colitis Epidemiology Study ACCESS Group . 2015. Environmental risk factors in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based case-control study in Asia-Pacific. Gut 64:1063–1071. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307410. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH, McGovern DP, Hui KY, Lee JC, Schumm LP, Sharma Y, Anderson CA, Essers J, Mitrovic M, Ning K, Cleynen I, Theatre E, Spain SL, Raychaudhuri S, Goyette P, Wei Z, Abraham C, Achkar JP, Ahmad T, Amininejad L, Ananthakrishnan AN, Andersen V, Andrews JM, Baidoo L, Balschun T, Bampton PA, Bitton A, Boucher G, Brand S, Buning C, Cohain A, Cichon S, D’Amato M, De Jong D, Devaney KL, Dubinsky M, Edwards C, Ellinghaus D, Ferguson LR, Franchimont D, Fransen K, Gearry R, Georges M, Gieger C, Glas J, Haritunians T, Hart A, et al. 2012. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 491:119–124. doi: 10.1038/nature11582. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H, Lesage S, Cézard JP, Belaiche J, Almer S, Tysk C, O’Morain CA, Gassull M, Binder V, Finkel Y, Cortot A, Modigliani R, Laurent-Puig P, Gower-Rousseau C, Macry J, Colombel JF, Sahbatou M, Thomas G. 2001. Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 411:599–603. doi: 10.1038/35079107. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, Nicolae DL, Chen FF, Ramos R, Britton H, Moran T, Karaliuskas R, Duerr RH, Achkar JP, Brant SR, Bayless TM, Kirschner BS, Hanauer SB, Nuñez G, Cho JH. 2001. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 411:603–606. doi: 10.1038/35079114. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

