Sirtuin1 is required for proper trophoblast differentiation and placental development in mice
- PMID: 29405961
- PMCID: PMC5805473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2017.12.002
Sirtuin1 is required for proper trophoblast differentiation and placental development in mice
Abstract
Introduction: Placental insufficiency, arising from abnormal trophoblast differentiation and function, is a major cause of fetal growth restriction. Sirtuin-1 (Sirt1) is a ubiquitously-expressed NAD-dependent protein deacetylase which plays a key role in numerous cellular processes, including cellular differentiation and metabolism. Though Sirt1 has been widely studied, its role in placentation and trophoblast differentiation is unclear.
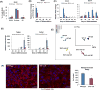
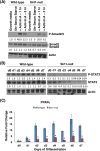
Method: Sirt1-heterozygous mice were mated and evaluated at various points during embryogenesis. In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry were used to further characterize the placental phenotype of Sirt1-null mice. Wild-type (WT) and Sirt1-null mouse trophoblast stem cell (TSC) lines were derived from e3.5 littermate blastocysts. These cells were then evaluated at various points following differentiation. Differentiation was evaluated by expression of lineage specific markers using qPCR and flow cytometry, as well as Matrigel invasion assays. Global gene expression changes were evaluated using microarray-based RNA profiling; changes in specific pathways were validated using qPCR and western blot.
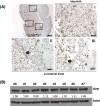
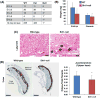
Results: In the absence of Sirt1, both embryos and placentas were small, with placentas showing abnormalities in both the labyrinthine layer and junctional zone. Sirt1-null TSCs exhibited an altered phenotype in both undifferentiated and differentiated states, phenotypes which corresponded to changes in pathways relevant to both TSC maintenance and differentiation. Specifically, Sirt1-null TSC showed blunted differentiation, and appeared to be suspended in an Epcamhigh trophoblast progenitor state.
Discussion: Our results suggest that Sirt1 is required for proper TSC differentiation and placental development.
Keywords: Differentiation; Fetal development; Fetal growth restriction; Placenta; Stem cells; Trophoblast.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

