A high resolution atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-quadrupole-orbitrap MS platform enables in situ analysis of biomolecules by multi-mode ionization and acquisition
- PMID: 29405984
- PMCID: PMC5805150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.12.045
A high resolution atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-quadrupole-orbitrap MS platform enables in situ analysis of biomolecules by multi-mode ionization and acquisition
Abstract
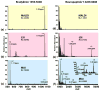
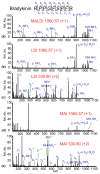
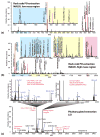
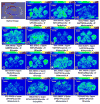
Introduced in 2000, atmospheric pressure (AP)/matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) has attracted substantial attention in the mass spectrometry community due to its ease of sample introduction and handling, interchangeability with ESI source and capability of analyzing volatile species. In this study, an AP/MALDI source with ultra-high spatial resolution was coupled to a Q Exactive HF orbitrap mass spectrometer for high resolution in situ analysis by MALDI, laserspray ionization (LSI) and matrix assisted ionization (MAI) without instrument modification. LSI and MAI generated multiply charged ions, which expanded the mass detection range and improved fragmentation efficiency. Full MS, targeted MS/MS, data dependent acquisition (DDA) and parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) acquisitions were performed on peptide and protein standards, tissue extracts and tissue sections for in depth characterization of various biomolecules. High resolution full MS and MS/MS images were obtained from crustacean and rat tissues with pixel size less than 30 μm. Overall, AP/MALDI-Q-Orbitrap is a fast scanning instrument that is capable of performing multiple types of ionization and multiple acquisition modes without instrument modification. This instrument platform provides an attractive alternative to other high resolution MALDI instruments.
Keywords: Atmospheric pressure ionization; High resolution accurate mass; Laserspray ionization; Mass spectrometry imaging; Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization; Neuropeptide.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix-assisted ionization vacuum for protein detection, fragmentation and PTM analysis on a high resolution linear ion trap-orbitrap platform.Anal Chim Acta. 2016 Apr 15;916:52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.02.018. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Anal Chim Acta. 2016. PMID: 27016438 Free PMC article.
-
Commercial intermediate pressure MALDI ion mobility spectrometry mass spectrometer capable of producing highly charged laserspray ionization ions.Anal Chem. 2011 Feb 1;83(3):678-84. doi: 10.1021/ac102779e. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21166462
-
Liquid Atmospheric Pressure Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using a Commercial Ion Source and Orbitrap Mass Analyzer.Anal Chem. 2024 Oct 8;96(40):15865-15870. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c04458. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39331381 Free PMC article.
-
Surface analysis of lipids by mass spectrometry: more than just imaging.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):329-53. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23623802 Review.
-
A perspective on MALDI alternatives-total solvent-free analysis and electron transfer dissociation of highly charged ions by laserspray ionization.J Mass Spectrom. 2010 May;45(5):471-85. doi: 10.1002/jms.1737. J Mass Spectrom. 2010. PMID: 20446310 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanosecond photochemically promoted click chemistry for enhanced neuropeptide visualization and rapid protein labeling.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 16;10(1):4697. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12548-0. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31619683 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosecond Photochemical Reaction (nsPCR) for Enhanced Mass Spectrometric Identification, Quantification, and Visualization of Metabolites and Neuropeptides.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2437:143-157. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2030-4_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34902146 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances of Ambient Mass Spectrometry Imaging and Its Applications in Lipid and Metabolite Analysis.Metabolites. 2021 Nov 15;11(11):780. doi: 10.3390/metabo11110780. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34822438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropeptidomics: Improvements in Mass Spectrometry Imaging Analysis and Recent Advancements.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021;22(2):158-169. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666201116115708. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021. PMID: 33200705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid Detection of Viral Envelope Lipids Using Lithium Adducts and AP-MALDI High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021 Sep 1;32(9):2322-2333. doi: 10.1021/jasms.1c00058. Epub 2021 Apr 22. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33886294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patterson NH, Doonan RJ, Daskalopoulou SS, Dufresne M, Lenglet S, Montecucco F, Thomas A, Chaurand P. 3D imaging mass spectrometry of lipids in atherosclerotic plaques: Open-source methods for reconstruction and analysis. Proteomics. 2016 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

