Is Use of a Psychological Workbook Associated With Improved Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Scores in Patients With Distal Radius Fracture?
- PMID: 29406451
- PMCID: PMC6260104
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000095
Is Use of a Psychological Workbook Associated With Improved Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Scores in Patients With Distal Radius Fracture?
Abstract
Background: Symptom intensity and magnitude of limitations correlate with stress, distress, and less effective coping strategies. It is unclear if interventions to target these factors can be used to improve outcomes after distal radius fracture in either the short- or longer term.
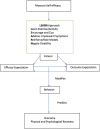
Questions/purposes: (1) Are there any factors (including the use of a workbook aimed at optimizing psychological response to injury, demographic, radiographic, medical, or psychosocial) associated with improved Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) and Numerical Rating Scale pain (NRS pain) scores at 6 weeks after management of distal radius fracture? (2) Are any of these factors associated with improved DASH and NRS pain scores at 6 months after management of distal radius fracture?
Methods: We conducted a double-blind randomized controlled trial comparing a workbook designed to optimize rehabilitation by improving psychological response to injury using recognized psychological techniques (the LEARN technique and goal setting) versus a workbook containing details of stretching exercises in the otherwise routine management of distal radius fracture. Patients older than 18 years of age with an isolated distal radius fracture were recruited within 3 weeks of injury from a single academic teaching hospital between March and August 2016. During recruitment, 191 patients who met the inclusion criteria were approached; 52 (27%) declined participation and 139 were enrolled. Eight patients (6%) were lost to followup by 6 weeks. The remaining cohort of 129 patients was included in the analysis. DASH scores and NRS pain scores were recorded at 6 weeks and 6 months after injury. Multivariable regression analysis was used to identify factors associated with outcome scores.
Results: At 6 weeks after distal radius fracture, when compared with an information-only workbook, use of a psychologic workbook was not associated with improved DASH (workbook DASH: 38 [range, 21-48]; control DASH: 35 [range, 21-53]; difference of medians: 3; p = 0.949) nor NRS pain scores (workbook NRS: 3 [range, 1-5]; control NRS: 2 [range, 1-4]; difference of medians: 1; p = 0.128). Improved DASH scores were associated with less radial shortening (β = 0.2, p = 0.009), less dorsal tilt (β = 0.2, p = 0.035), and nonoperative treatment (β = 0.2, p = 0.027). Improved NRS pain scores were associated with nonoperative treatment (β = 0.2, p = 0.021) and no posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (β = 0.2, p = 0.046). At 6 months, use of a psychologic workbook was not associated with improved DASH (workbook DASH: 11 [range, 5-28]; control DASH: 11 [range, 3-20]; difference of medians: 0; p = 0.367) nor NRS pain scores (workbook NRS: 1 [range, 0-2]; control NRS: 1 [range, 0-2]; difference of medians: 0; p = 0.704). Improved DASH score at 6 months was associated with having fewer medical comorbidities (β = 0.3, p < 0.001) and lower enrollment PTSD (β = 0.3, p < 0.011). Lower NRS pain scores at 6 months were associated with having fewer medical comorbidities (β = 0.2, p = 0.045), lower enrollment PTSD (β = 0.3, p = 0.008), and lower enrollment Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia (β = 0.2, p = 0.042).
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that there is no benefit from the untargeted use of a psychological workbook based on the LEARN approach and goal-setting strategies in patients with distal radius fracture. Future research should investigate if there is a subgroup of patients with a negative psychological response to injury that benefits from psychological intervention and, if so, how best to identify these patients and intervene.
Level of evidence: Level II, therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures
References
-
- Alarcon LH, Germain A, Clontz AS, Roach E, Nicholas DH, Zenati MS, Peitzman AB, Perry JL. Predictors of acute posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms following civilian trauma: highest incidence and severity of symptoms after assault. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72:629. - PubMed
-
- Barlow JH, Williams B, Wright C. The Generalized Self-Efficacy Scale in people with arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 1996;9:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Becher S, Smith M, Ziran B. Orthopaedic trauma patients and depression: a prospective cohort. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28:e242–246. - PubMed
-
- Bosse MJ, MacKenzie EJ, Kellam JF, Burgess AR, Webb LX, Swiontkowski MF, Sanders RW, Jones AL, McAndrew MP, Patterson BM, McCarthy ML, Travison TG, Castillo RC. An analysis of outcomes of reconstruction or amputation after leg- threatening injuries. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1924–1931. - PubMed
-
- Bot AGJ. Bekkers S, Herndon JH, Mudgal CS, Jupiter JB, Ring D. Determinants of disability after proximal interphalangeal joint sprain or dislocation. Psychosomatics. 2014;55:595–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous