The Growing Threat of Antibiotic Resistance in Children
- PMID: 29406971
- PMCID: PMC5927609
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idc.2017.11.001
The Growing Threat of Antibiotic Resistance in Children
Abstract
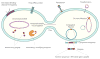
Antimicrobial resistance is a global public health threat and a danger that continues to escalate. These menacing bacteria are having an impact on all populations; however, until recently, the increasing trend in drug-resistant infections in infants and children has gone relatively unrecognized. This article highlights the current clinical and molecular data regarding infection with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in children, with an emphasis on transmissible resistance and spread via horizontal gene transfer.
Keywords: Bacteria; Child; Drug resistance; Epidemiology; Genetic structures; Infection; Public health; β-Lactamases.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- White DG, Zhao S, Sudler R, et al. The isolation of antibiotic-resistant salmonella from retail ground meats. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1147–54. - PubMed
-
- Toleman MA, Walsh TR. Combinatorial events of insertion sequences and ICE in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011;35:912–35. - PubMed
-
- Woodford N, Ellington MJ. The emergence of antibiotic resistance by mutation. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007;13:5–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

