Prediabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiology and Interventions for Prevention and Risk Reduction
- PMID: 29407055
- PMCID: PMC5806140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2017.10.001
Prediabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiology and Interventions for Prevention and Risk Reduction
Abstract
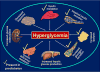
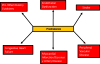
Prediabetes is a state characterized by impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance. This review discusses the pathophysiology and macrovascular complications of prediabetes. The pathophysiologic defects underlying prediabetes include insulin resistance, alpha- and beta-cell dysfunction, increased lipolysis, inflammation, and suboptimal incretin effect. Recent studies have revealed that the long-term complications of diabetes manifest in some people with prediabetes; these complications include microvascular and macrovascular disorders. Finally, we present an overview of randomized control trials aimed at preventing progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes and discuss their implications for macrovascular risk reduction.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Impaired fasting glucose; Impaired glucose tolerance; Macrovascular; Prediabetes complications.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization. Geneva (Switzerland): 2016. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2016.
-
- Dall TM, Yang W, Halder P, et al. The Economic Burden of Elevated Blood Glucose Levels in 2012. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:3172–3179. - PubMed
-
- Zhang P, Zhang X, Brown J, et al. Global healthcare expenditure on diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:293–301. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Abdul-Ghani M. Assessment treatment of cardiovascular risk in prediabetes: impaired glucose tolerance impaired fasting glucose. Am J Cardiol. 2011;108:3B–24B. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

