Metabolic/inflammatory/vascular comorbidity in psychiatric disorders; soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) as a possible new target
- PMID: 29407524
- PMCID: PMC5860823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.01.010
Metabolic/inflammatory/vascular comorbidity in psychiatric disorders; soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) as a possible new target
Abstract
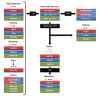
The common and severe psychiatric disorders, including major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD), are associated with inflammation, oxidative stress and changes in peripheral and brain lipid metabolism. Those pathways are implicated in the premature development of vascular and metabolic comorbidities, which account for considerable morbidity and mortality, including increased dementia risk. During endoplasmic reticulum stress, the soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) enzyme converts anti-inflammatory fatty acid epoxides generated by cytochrome p450 enzymes into their corresponding and generally less anti-inflammatory, or even pro-inflammatory, diols, slowing the resolution of inflammation. The sEH enzyme and its oxylipin products are elevated post-mortem in MDD, BD and schizophrenia. Preliminary clinical data suggest that oxylipins increase with symptoms in seasonal MDD and anorexia nervosa, requiring confirmation in larger studies and other cohorts. In rats, a soluble sEH inhibitor mitigated the development of depressive-like behaviors. We discuss sEH inhibitors under development for cardiovascular diseases, post-ischemic brain injury, neuropathic pain and diabetes, suggesting new possibilities to address the mood and cognitive symptoms of psychiatric disorders, and their most common comorbidities.
Keywords: Dementia; Depression; Diabetes; Drug development; ER stress; Heart disease; Inflammasome; Lipidomics; Metabolism; Mitochondrial dysfunction; NLRP3; Neurodegeneration; Neuroprogression; Obesity; Omega-3 fatty acids; Soluble epoxide hydrolase; Stroke.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson G. Linking the biological underpinnings of depression: Role of mitochondria interactions with melatonin, inflammation, sirtuins, tryptophan catabolites, DNA repair and oxidative and nitrosative stress, with consequences for classification and cognition. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2017 - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Roberts-Twillie JV, Barta PE, Kumar AJ, Harris GJ, Geer M, Peyser CE, Pearlson GD. Basal ganglia volumes and white matter hyperintensities in patients with bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1994;151:687–693. - PubMed
-
- Berk M, Kapczinski F, Andreazza AC, Dean OM, Giorlando F, Maes M, Yucel M, Gama CS, Dodd S, Dean B, Magalhaes PV, Amminger P, McGorry P, Malhi GS. Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews. 2011;35:804–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

