Individual assets and problem behaviors in at-risk adolescents: A longitudinal cross-lagged analysis
- PMID: 29408099
- PMCID: PMC5857248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2018.01.008
Individual assets and problem behaviors in at-risk adolescents: A longitudinal cross-lagged analysis
Abstract
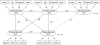
Autoregressive cross-lagged structural equation modeling was conducted to examine longitudinal relationships between individual assets (social competence, positive values and identity) and problem behaviors in 373 adolescents (174 boys, 199 girls) who participated in a prospective study on the effects of prenatal cocaine exposure from birth. More behavioral problems at age 12 were related to fewer individual assets at age 15, while greater individual assets were related to more behavioral problems, with a non-significant yet nuanced (p = .076) gender difference. More problem behaviors were associated with decreased individual assets in girls, yet greater individual assets were associated with more problem behaviors in boys. Efforts to promote individual assets may not lower the risk of engaging in problem behaviors especially among boys. Continued studies into adulthood will uncover how individual assets and problem behaviors in childhood and adolescence may affect social and vocational adjustment in this high risk population.
Keywords: Adolescents; Cross-lagged; Individual assets; Problem behavior; Structural equation modeling.
Copyright © 2018 The Foundation for Professionals in Services for Adolescents. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Profiles of individual assets and mental health symptoms in at-risk early adolescents.J Adolesc. 2019 Aug;75:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2019.06.012. Epub 2019 Jul 6. J Adolesc. 2019. PMID: 31288121 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on early sexual behavior: Gender difference in externalizing behavior as a mediator.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015 Aug 1;153:59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015. PMID: 26088698 Free PMC article.
-
From childhood adversity to problem behaviors: Role of psychological and structural social integration.Pediatr Int. 2018 Jan;60(1):23-29. doi: 10.1111/ped.13436. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Pediatr Int. 2018. PMID: 29059487
-
The relation between behavioral problems and social competence: A correlational Meta-analysis.BMC Psychiatry. 2019 Nov 9;19(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2343-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31706279 Free PMC article.
-
Problem behavior of internationally adopted adolescents: a review and meta-analysis.Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003 Mar-Apr;11(2):64-77. doi: 10.1080/10673220303955. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12868507 Review.
Cited by
-
Internal assets in low-income urban adolescents from 12 to 17 years: Gender variation.J Res Adolesc. 2025 Mar;35(1):e70018. doi: 10.1111/jora.70018. J Res Adolesc. 2025. PMID: 40134339 Free PMC article.
-
Profiles of individual assets and mental health symptoms in at-risk early adolescents.J Adolesc. 2019 Aug;75:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2019.06.012. Epub 2019 Jul 6. J Adolesc. 2019. PMID: 31288121 Free PMC article.
-
Association of perceived stress and self-control with health-promoting behaviors in adolescents: A cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(34):e11880. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011880. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30142784 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways from prenatal cocaine exposure to adult substance use and behavior.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2024 Mar-Apr;102:107335. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2024.107335. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2024. PMID: 38373556 Free PMC article.
-
Substance use and individual assets in urban adolescents: Subgroups and correlates in emerging adulthood.J Adolesc. 2022 Jun;94(4):684-697. doi: 10.1002/jad.12056. Epub 2022 May 25. J Adolesc. 2022. PMID: 35615786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abt T, Winship C. What works in reducing community violence: A meta-review and field study for the northern triangle. Washington, DC: United States Agency for International Development; 2016. Retrieved from https://www.usaid.gov/sites/default/files/USAID-2016-What-Works-in-Reduc....
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families; 2001.
-
- Bada HS, Bann CM, Bauer CR, Shankaran S, Lester B, LaGasse L, et al. Higgins R. Preadolescent behavior problems after prenatal cocaine exposure: Relationship between teacher and caretaker ratings (Maternal Lifestyle Study) Neurotoxicology and Teratology. 2011;33(1):78–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2010.06.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

