Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 29408694
- PMCID: PMC5893377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.01.019
Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
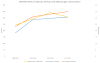
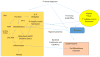
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome; its rising prevalence parallels the rise in obesity and diabetes. Historically thought to result from overnutrition and a sedentary lifestyle, recent evidence suggests that diets high in sugar (from sucrose and/or high-fructose corn syrup [HFCS]) not only increase the risk of NAFLD, but also non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Herein, we review the experimental and clinical evidence that fructose precipitates fat accumulation in the liver, due to both increased lipogenesis and impaired fat oxidation. Recent evidence suggests that the predisposition to fatty liver is linked to the metabolism of fructose by fructokinase C, which results in ATP consumption, nucleotide turnover and uric acid generation that mediate fat accumulation. Alterations to gut permeability, the microbiome, and associated endotoxemia contribute to the risk of NAFLD and NASH. Early clinical studies suggest that reducing sugary beverages and total fructose intake, especially from added sugars, may have a significant benefit on reducing hepatic fat accumulation. We suggest larger, more definitive trials to determine if lowering sugar/HFCS intake, and/or blocking uric acid generation, may help reduce NAFLD and its downstream complications of cirrhosis and chronic liver disease.
Keywords: Hepatic inflammation; Hepatic steatosis; Insulin resistance; Sugar consumption; Uric acid.
Copyright © 2018 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Yracheta JM, Alfonso J, Lanaspa MA, Roncal-Jimenez C, Johnson SB, Sanchez-Lozada LG, et al. Hispanic Americans living in the United States and their risk for obesity, diabetes and kidney disease: Genetic and environmental considerations. Postgrad Med. 2015;127(5):503–10. - PubMed
-
- Yracheta JM, Lanaspa MA, Le MT, Abdelmalak MF, Alfonso J, Sanchez-Lozada LG, et al. Diabetes and Kidney Disease in American Indians: Potential Role of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90(6):813–23. - PubMed
-
- Johnson RJ, Lanaspa MA, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Rivard CJ, Bjornstad PS, Merriman T, et al. Fat storage syndrome in Pacific peoples: a combination of environment and genetics? Pac Health Dialog. 2014;20(1):11–6. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald I. Influence of fructose and glucose on serum lipid levels in men and pre- and postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1966;18(5):369–72. - PubMed