Effect of maternal height on caesarean section and neonatal mortality rates in sub-Saharan Africa: An analysis of 34 national datasets
- PMID: 29408912
- PMCID: PMC5800647
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192167
Effect of maternal height on caesarean section and neonatal mortality rates in sub-Saharan Africa: An analysis of 34 national datasets
Abstract
Rationale: The lifecycle perspective reminds us that the roots of adult ill-health may start in-utero or in early childhood. Nutritional and infectious disease insults in early life, the critical first 1000 days, are associated with stunting in childhood, and subsequent short adult stature. There is limited or no opportunity for stunted children above 2 years of age to experience catch-up growth. Some previous research has shown short maternal height to lead to adverse birth outcomes. In this paper, we document the association between maternal height and caesarean section, and between maternal height and neonatal mortality in 34 sub-Saharan African countries. We also explore the appropriate height cut-offs to use. Our paper contributes arguments to support a focus on preventing non-communicable risk factors, namely early childhood under-nutrition, as part of the fight to reduce caesarean section rates and other adverse maternal and newborn health outcomes, particularly neonatal mortality. We focus on the Sub-Saharan Africa region because it carries the highest burden of maternal and neonatal ill-health.
Methods: We used the most recent Demographic and Health Survey for 34 sub-Saharan African countries. The distribution of heights of women who had given birth in the 5 years before the survey was explored. We adopted the following cut-offs: Very Short (<145.0cm), Short (145.0-149.9cm), Short-average (150.0-154.9cm), Average (155.0-159.9cm), Average-tall (160.0-169.9cm) and Tall (≥170.0cm). Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess the contribution of maternal stature to the odds ratio of caesarean section delivery, adjusting for other exposures, such as age at index birth, residence, maternal BMI, maternal education, wealth index quintile, previous caesarean section, multiple birth, birth order and country of survey. We also look at its contribution to neonatal mortality adjusting for age at index birth, residence, maternal BMI, maternal education, wealth index quintile, multiple birth, birth order and country of survey.
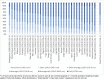
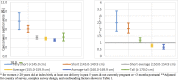
Results: There was a gradual increase in the rate of caesarean section with decreasing maternal height. Compared to women of Average height (155.0-159.9cm), taller women were protected. The adjusted odds ratio (aOR) for Tall women was 0.67 (95% CI:0.52-0.87) and for Average-tall women was 0.78 (95% CI:0.69-0.89). Compared to women of Average height, shorter women were at increased risk. The aOR for Short-average women was 1.19 (95% CI:1.03-1.37), for Short women was 2.06 (95% CI:1.71-2.48), and for Very Short women was 2.50 (95% CI:1.85-3.38). There was evidence that compared to Average height women, Very Short and Short women had increased odds of experiencing a neonatal death aOR = 1.95 (95% CI 1.17-3.25) and aOR = 1.66 (95% CI 1.20-2.28) respectively. When we focused on the period of highest risk, the day of delivery and first postnatal day, these aORs increased to 2.36 (95% CI 1.57-3.55) and 2.34 (95% CI 1.19-4.60) respectively. The aORs for the first week of life (early neonatal mortality) were 1.90 (95% CI 1.07-3.36) and 1.83 (95% CI 1.30-2.59) respectively.
Conclusions: Short stature is associated with an increased prevalence of caesarean section and neonatal mortality, particularly on the newborn's first days. These results are even more striking because we know that caesarean section rates tend to be higher among wealthier and more educated women, who are often taller and that the same patterns may hold for neonatal survival; in such cases, adjusting for wealth, education and urban residence would attenuate these associations. Caesarean sections can be lifesaving operations; however, they cost the health system and families more, and are associated with worse health outcomes. We suggest that our findings be used to argue for policies targeting stunting in infant girls and potential catch-up growth in adolescence and early adulthood, aiming to increase their adult height and thus decrease their subsequent risk of experiencing caesarean section and adverse birth outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caesarean section and subsequent fertility in sub-Saharan Africa.BJOG. 2006 Mar;113(3):276-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00846.x. BJOG. 2006. PMID: 16487198
-
Maternal and perinatal outcomes among nulliparous adolescents in low- and middle-income countries: a multi-country study.BJOG. 2013 Dec;120(13):1622-30; discussion 1630. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.12391. Epub 2013 Aug 7. BJOG. 2013. PMID: 23924217
-
Maternal and perinatal outcomes of extreme obesity in pregnancy.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2013 Jul;35(7):606-611. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30879-3. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2013. PMID: 23876637
-
Prevalence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Womens Health (Lond). 2020 Jan-Dec;16:1745506520973105. doi: 10.1177/1745506520973105. Womens Health (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33334273 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal and perinatal mortality and complications associated with caesarean section in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet. 2019 May 11;393(10184):1973-1982. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32386-9. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 30929893
Cited by
-
Caesarean delivery and its association with educational attainment, wealth index, and place of residence in Sub-Saharan Africa: a meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 1;12(1):5554. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09567-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35365718 Free PMC article.
-
Second-trimester anthropometric estimators of cesarean section: the agreement between body roundness index, body mass index, body fat percentage, and waist circumference.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 May 10;25(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07643-8. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40348957 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Cesarean Section Among Nurses: Predictors and Effect on Exclusive Breastfeeding.SAGE Open Nurs. 2023 Dec 17;9:23779608231214214. doi: 10.1177/23779608231214214. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2023. PMID: 38116066 Free PMC article.
-
Variations in the prevalence of caesarean section deliveries in India between 2016 and 2021 - an analysis of Tamil Nadu and Chhattisgarh.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Aug 30;23(1):622. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-05928-4. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37649006 Free PMC article.
-
A biosocial analysis of perinatal and late neonatal mortality among Indigenous Maya Kaqchikel communities in Tecpán, Guatemala: a mixed-methods study.BMJ Glob Health. 2024 Apr 17;9(4):e013940. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2023-013940. BMJ Glob Health. 2024. PMID: 38631704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darnton-Hill I, Nishida C, James WP, A life course approach to diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. Public Health Nutr, 2004. 7(1A): p. 101–21. - PubMed
-
- Martorell R, Body Size, Adaptation and Function. Human Organization, 1989. 48(1): p. 15–20.
-
- Perkins JM, Subramanian SV, Davey Smith G, Özaltin E, Adult height, nutrition, and population health. Nutrition Reviews, 2016. 74(3): p. 149–165. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuv105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Subramanian SV, Özaltin E, Finlay JE, Height of nations: a socioeconomic analysis of cohort differences and patterns among women in 54 low- to middle-income countries. PLoS One, 2011. 6(4): p. e18962 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018962 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

