DNA methylome profiling at single-base resolution through bisulfite sequencing of 5mC-immunoprecipitated DNA
- PMID: 29409498
- PMCID: PMC5801686
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-017-0409-7
DNA methylome profiling at single-base resolution through bisulfite sequencing of 5mC-immunoprecipitated DNA
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: DNA methylome profiling at single-base resolution through bisulfite sequencing of 5mC-immunoprecipitated DNA.BMC Biotechnol. 2020 May 11;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12896-020-00619-w. BMC Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32393318 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Detection of DNA methylome at single-base resolution is a significant challenge but promises to shed considerable light on human disease etiology. Current technologies could not detect DNA methylation genome-wide at single-base resolution with small amount of sequencing data and could not avoid detecting the methylation of repetitive elements which are considered as "junk DNA".
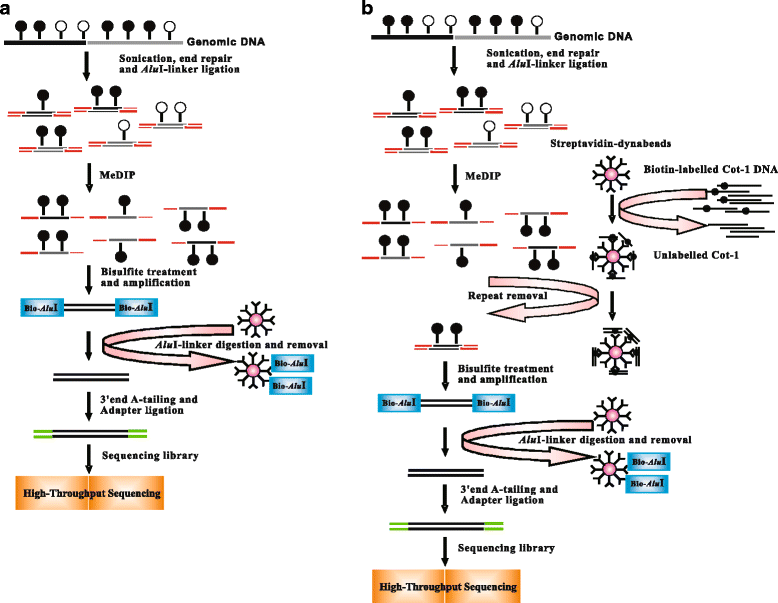
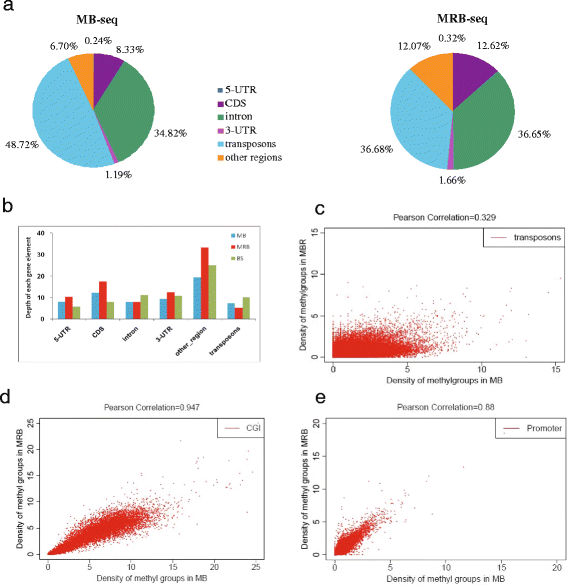
Methods: In this study, we have developed a novel DNA methylome profiling technology named MB-seq with its ability to identify genome-wide 5mC and quantify DNA methylation levels by introduced an assistant adapter AluI-linker This linker can be ligated to sonicated DNA and then be digested after the bisulfite treatment and amplification, which has no effect of MeDIP enrichment. Because many researchers are interested in investigating the methylation of functional regions such as promoters and gene bodies, we have also developed a novel alternative method named MRB-seq, which can be used to investigate the DNA methylation of functional regions by removing the repeats with Cot-1 DNA.
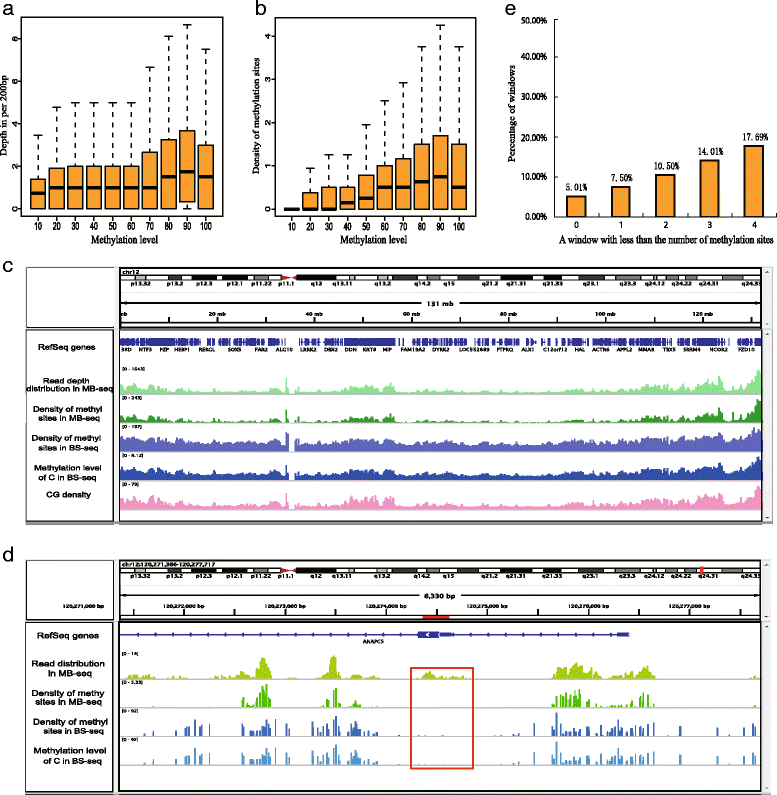
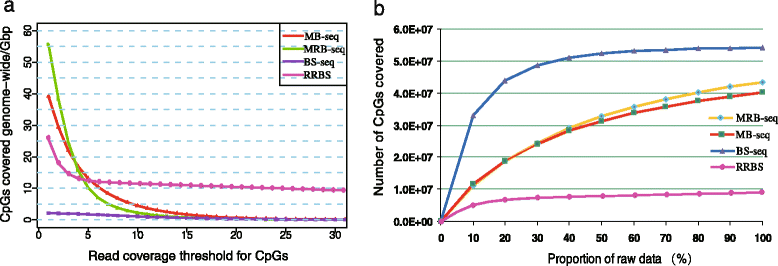
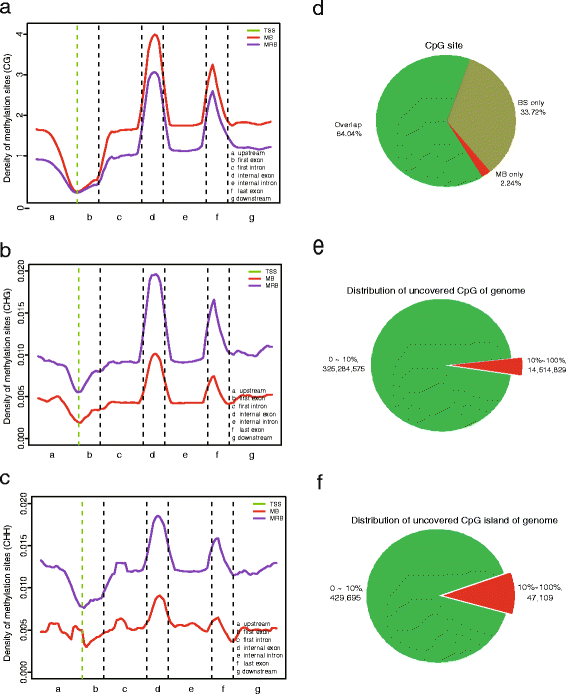
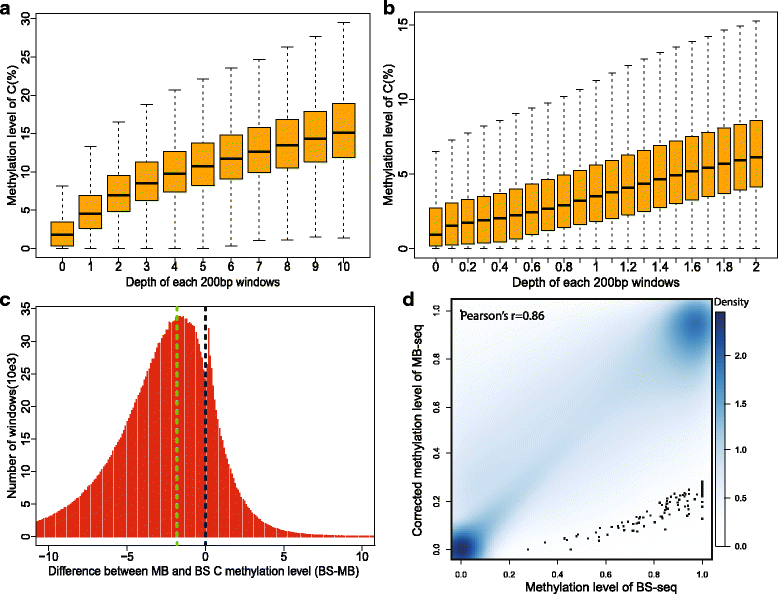
Results: In this study, we have developed MB-seq, a novel DNA methylome profiling technology combining MeDIP-seq with bisulfite conversion, which can precisely detect the 5mC sites and determine their DNA methylation level at single-base resolution in a cost-effective way. In addition, we have developed a new alternative method, MRB-seq (MeDIP-repetitive elements removal-bisulfite sequencing), which interrogates 5mCs in functional regions by depleting nearly half of repeat fragments enriched by MeDIP. Comparing MB-seq and MRB-seq to whole-genome BS-seq using the same batch of DNA from YH peripheral blood mononuclear cells. We found that the sequencing data of MB-seq and MRB-seq almost reaches saturation after generating 7-8 Gbp data, whereas BS-seq requires about 100 Gbp data to achieve the same effect. In comparison to MeDIP-seq and BS-seq, MB-seq offers several key advantages, including single-base resolution, discriminating the methylated sites within a CpG and non-CpG pattern and overcoming the false positive of MeDIP-seq due to the non-specific binding of 5-methylcytidine antibody to genomic fragments.
Conclusion: Our novel developed method MB-seq can accelerate the decoding process of DNA methylation mechanism in human diseases because it requires 7-8 Gbp data to measure human methylome with enough coverage and sequencing depth, affording it a direct and practical application in the study of multiple samples. In addition, we have also provided a novel alternative MRB-seq method, which removes most repetitive sequences and allows researchers to genome-wide characterize DNA methylation of functional regions.
Keywords: DNA methylome; MB-seq; MRB-seq; Novel technology; Single-base resolution.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines. This study was approved by written consent from the ethical committee of the Beijing Aviation General Hospital. Relevant informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interest regarding to publishing this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

