Fusobacterium nucleatum and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Epidemiological and mechanistic evidence
- PMID: 29409815
- PMCID: PMC6750227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2018.01.008
Fusobacterium nucleatum and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Epidemiological and mechanistic evidence
Abstract
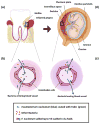
Fusobacterium nucleatum is a Gram-negative anaerobic oral commensal associated with periodontal disease. F. nucleatum has been implicated in a wide spectrum of systemic diseases, including oral, gastro-intestinal, rheumatologic, and vascular pathologies. As pregnancy risk has been linked to periodontal disease, there has also been significant research into the effects of periodontal disease on adverse pregnancy outcomes. This article reviews the epidemiological and mechanistic evidence of the role of F. nucleatum in adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Keywords: Chorioamnionitis; FadA; Fusobacterium nucleatum; Neonatal sepsis; Oral anaerobe; Placenta; Pregnancy complications; Preterm birth; Stillbirth; VE-cadherin.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW. Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1500–1507. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg RL, Thompson C. The infectious origins of stillbirth. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189:861–873. - PubMed
-
- Premature Birth Report Card. March of Dimes Perinatal Data Center; 2016.
-
- McCormick MC, Behrman RE. The quiet epidemic of premature birth: commentary on a recent Institute of Medicine report. Ambul Pediatr. 2007;7:8–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

