Organoids with cancer stem cell-like properties secrete exosomes and HSP90 in a 3D nanoenvironment
- PMID: 29415026
- PMCID: PMC5802492
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191109
Organoids with cancer stem cell-like properties secrete exosomes and HSP90 in a 3D nanoenvironment
Abstract
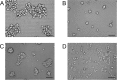
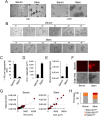
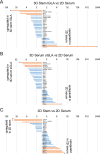
Ability to form cellular aggregations such as tumorspheres and spheroids have been used as a morphological marker of malignant cancer cells and in particular cancer stem cells (CSC). However, the common definition of the types of cellular aggregation formed by cancer cells has not been available. We examined morphologies of 67 cell lines cultured on three dimensional morphology enhancing NanoCulture Plates (NCP) and classified the types of cellular aggregates that form. Among the 67 cell lines, 49 cell lines formed spheres or spheroids, 8 cell lines formed grape-like aggregation (GLA), 8 cell lines formed other types of aggregation, and 3 cell lines formed monolayer sheets. Seven GLA-forming cell lines were derived from adenocarcinoma among the 8 lines. A neuroendocrine adenocarcinoma cell line PC-3 formed asymmetric GLA with ductal structures on the NCPs and rapidly growing asymmetric tumors that metastasized to lymph nodes in immunocompromised mice. In contrast, another adenocarcinoma cell line DU-145 formed spheroids in vitro and spheroid-like tumors in vivo that did not metastasize to lymph nodes until day 50 after transplantation. Culture in the 3D nanoenvironment and in a defined stem cell medium enabled the neuroendocrine adenocarcinoma cells to form slowly growing large organoids that expressed multiple stem cell markers, neuroendocrine markers, intercellular adhesion molecules, and oncogenes in vitro. In contrast, the more commonly used 2D serum-contained environment reduced intercellular adhesion and induced mesenchymal transition and promoted rapid growth of the cells. In addition, the 3D stemness nanoenvironment promoted secretion of HSP90 and EpCAM-exosomes, a marker of CSC phenotype, from the neuroendocrine organoids. These findings indicate that the NCP-based 3D environment enables cells to form stem cell tumoroids with multipotency and model more accurately the in vivo tumor status at the levels of morphology and gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Welsh M, Mangravite L, Medina MW, Tantisira K, Zhang W, Huang RS, et al. Pharmacogenomic discovery using cell-based models. Pharmacol Rev. 2009;61(4):413–29. doi: 10.1124/pr.109.001461 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mizushima H, Wang X, Miyamoto S, Mekada E. Integrin signal masks growth-promotion activity of HB-EGF in monolayer cell cultures. J Cell Sci. 2009;122(Pt 23):4277–86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.054551 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baker BM, Chen CS. Deconstructing the third dimension: how 3D culture microenvironments alter cellular cues. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 13):3015–24. doi: 10.1242/jcs.079509 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumar M, Allison DF, Baranova NN, Wamsley JJ, Katz AJ, Bekiranov S, et al. NF-kappaB regulates mesenchymal transition for the induction of non-small cell lung cancer initiating cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e68597 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068597 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arai K, Eguchi T, Rahman MM, Sakamoto R, Masuda N, Nakatsura T, et al. A Novel High-Throughput 3D Screening System for EMT Inhibitors: A Pilot Screening Discovered the EMT Inhibitory Activity of CDK2 Inhibitor SU9516. PLoS One. 2016;11(9):e0162394 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162394 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

