Incidence and characteristics of kidney stones in patients with horseshoe kidney: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29416282
- PMCID: PMC5791465
- DOI: 10.4103/UA.UA_76_17
Incidence and characteristics of kidney stones in patients with horseshoe kidney: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The horseshoe kidney (HSK) is the most common type of renal fusion anomaly. The incidence and characteristics of kidney stones in patients with HSK are not well studied. The aim of this meta-analysis was to evaluate the incidence and types of kidney stones in patients with HSK.
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed using MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews from the databases' inception through November 2016. Studies assessing the incidence and types of kidney stones in patients with HSK were included. We applied a random-effects model to estimate the incidence of kidney stones. The study protocol was registered with PROSPERO (International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews; no. CRD42016052037).
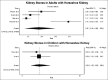
Results: A total of 14 observational studies with 943 patients (522 adults and 421 pediatric) with HSK were enrolled. The estimated pooled incidence of kidney stones was 36% (95% confidence interval [CI], 15%-59%) in adults with the HSK. Kidney stones were less common in pediatric patients with HSK with an estimated pooled incidence of 3% (95% CI, 2%-5%). The mean age of adult stone formers with HSK was 44.9 ± 6.2 years, and 75% were males. Within reported studies, 89.2% of kidney stones were calcium-based stones (64.2% calcium oxalate [CaOx], 18.8% calcium phosphate [CaP], and 6.2% mixed CaOx/CaP), followed by struvite stones (4.2%), uric acid stones (3.8%), and others (2.8%).
Conclusions: Kidney stones are very common in adult patients with HSK with an estimated incidence of 36%. Calcium-based stones are the most prevalent kidney stones in adults with HSKs. These findings may impact the prevention and clinical management of kidney stones in patients with HSK.
Keywords: Horseshoe kidney; incidence; kidney stones; nephrolithiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lieske JC, Peña de la Vega LS, Slezak JM, Bergstralh EJ, Leibson CL, Ho KL, et al. Renal stone epidemiology in Rochester, Minnesota: An update. Kidney Int. 2006;69:760–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous