Replacing sedentary time with physical activity: a 15-year follow-up of mortality in a national cohort
- PMID: 29416378
- PMCID: PMC5790069
- DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S151613
Replacing sedentary time with physical activity: a 15-year follow-up of mortality in a national cohort
Abstract
Background: Sedentary behavior is associated with health risks in adults. The potential benefits of reducing sedentary time may be dependent not only on decrease per se, but also on the type of activity it replaces. Few longitudinal studies have investigated the effects on mortality when replacing objectively assessed sedentary time with another physical activity (PA) behavior.
Objective: To investigate the effects of replacing objectively assessed sedentary time with time in light-intensity PA or moderate-vigorous PA (MVPA) on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality or cancer mortality in a cohort with 15 years follow-up time.
Methods: In total, 851 women and men from the population-based Sweden Attitude Behaviour and Change study were included. Time spent sedentary, in light-intensity PA and in MVPA were assessed using an Actigraph 7164 accelerometer. Mortality data were obtained from Swedish registers. Cox proportional hazards models estimated hazard ratios (HR) of mortality with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and isotemporal substitution models were used to estimate the effect of replacing sedentary behavior with PA for the same amount of time.
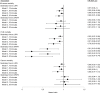
Results: Over a follow-up of 14.2 years (SD 1.9) with 12,117 person-years at risk, 79 deaths occurred, 24 deaths from CVD, 27 from cancer, and 28 from other causes. Replacing 30 minutes/day of sedentary time with light-intensity PA was associated with significant reduction in all-cause mortality risk (HR: 0.89, 95% CI: 0.81-0.98) and CVD mortality risk (HR: 0.76, 95% CI: 0.63-0.92). Replacing 10 minutes of sedentary time with MVPA was associated with reduction in CVD mortality risk (HR: 0.62, 95% CI: 0.42-0.91). No statistically significant reductions were found for cancer mortality.
Conclusion: This statistical modelling study suggests that replacing sedentary time with light-intensity PA could have beneficial effect on both all-cause mortality and CVD mortality. Replacing sedentary time with MVPA could reduce CVD mortality.
Keywords: accelerometry; isotemporal substitution; light intensity; moderate-to-vigorous intensity; prospective; sedentary behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Wilmot EG, Edwardson CL, Achana FA, et al. Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2012;55(11):2895–2905. - PubMed
-
- Thorp AA, Owen N, Neuhaus M, Dunstan DW. Sedentary behaviors and subsequent health outcomes in adults a systematic review of longitudinal studies, 1996–2011. Am J Prev Med. 2011;41(2):207–215. - PubMed
-
- Chau JY, Grunseit A, Midthjell K, et al. Sedentary behaviour and risk of mortality from all-causes and cardiometabolic diseases in adults: evidence from the HUNT3 population cohort. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(11):737–742. - PubMed
-
- Buman MP, Winkler EA, Kurka JM, et al. Reallocating time to sleep, sedentary behaviors, or active behaviors: associations with cardiovascular disease risk biomarkers, NHANES 2005–2006. Am J Epidemiol. 2014;179(3):323–334. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

