The Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Bone Fracture Healing
- PMID: 29416527
- PMCID: PMC5787540
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00006
The Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Bone Fracture Healing
Abstract
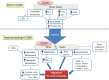
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disease known by the presence of elevated blood glucose levels. Nowadays, it is perceived as a worldwide epidemic, with a very high socioeconomic impact on public health. Many are the complications caused by this chronic disorder, including a negative impact on the cardiovascular system, kidneys, eyes, muscle, blood vessels, and nervous system. Recently, there has been increasing evidence suggesting that T2DM also adversely affects the skeletal system, causing detrimental bone effects such as bone quality deterioration, loss of bone strength, increased fracture risk, and impaired bone healing. Nevertheless, the precise mechanisms by which T2DM causes detrimental effects on bone tissue are still elusive and remain poorly studied. The aim of this review was to synthesize current knowledge on the different factors influencing the impairment of bone fracture healing under T2DM conditions. Here, we discuss new approaches used in recent studies to unveil the mechanisms and fill the existing gaps in the scientific understanding of the relationship between T2DM, bone tissue, and bone fracture healing.
Keywords: bone regeneration; bone turnover; fracture healing; fracture risk; hyperglycemia; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Lecka-Czernik B, Stechschulte LA, Czernik PJ, Dowling AR. High bone mass in adult mice with diet-induced obesity results from a combination of initial increase in bone mass followed by attenuation in bone formation; implications for high bone mass and decreased bone quality in obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol (2014) 410:35–41.10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

