The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor dactolisib elicits anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 29416647
- PMCID: PMC5787502
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23091
The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor dactolisib elicits anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo
Erratum in
-
Correction: The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor dactolisib elicits anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2018 Mar 30;9(24):17255. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25063. eCollection 2018 Mar 30. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29683149 Free PMC article.
Abstract
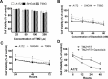
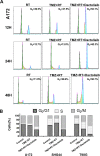
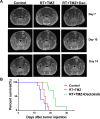
Glioblastomas (GBMs) are among the most malignant of all human tumors and have poor prognosis. The current standard of care (SOC) includes maximal surgical tumor resection followed by adjuvant temozolomide (TMZ) and concomitant radiotherapy (RT). However, even with this treatment, the 5-year survival rate is less than 10%, and thus, follow-up treatment is required to improve efficacy. In GBMs as well as many other solid cancers, PI3K/mTOR signaling is overactivated. Therefore, multiple tumor-based PI3K inhibitors have been studied in various cancers. In the current study, we investigated the effect of the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor dactolisib on TMZ+RT treatment in three human GBM cell lines and a orthotopic xenograft model. Dactolisib alone induced cytotoxicity and pro-apoptotic effects, which act as antitumor factors. Combined with SOC treatment, dactolisib inhibited cell viability, induced enhanced pro-apoptotic effect, and attenuated migration/invasion in all three cell lines, thereby enhancing the SOC therapeutic effect. Protein microarray analysis showed that A172 cells treated with TMZ+RT+dactolisib had higher p27 and lower Bcl-2 expression than other groups. Moreover, in the xenograft model, oral dactolisib combined with TMZ+RT inhibited tumor growth and prolonged survival. Thus, SOC combined with dactolisib shows potent anti-tumor activity and has promising potential for solid tumor treatment.
Keywords: chemotherapy; dactolisib (NVP-BEZ235); dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor; glioblastoma; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Network TC. Corrigendum: Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature. 2013;494:506. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11903. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eom KY, Cho BJ, Choi EJ, Kim JH, Chie EK, Wu HG, Kim IH, Paek SH, Kim JS, Kim IA. The Effect of Chemoradiotherapy with SRC Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, PP2 and Temozolomide on Malignant Glioma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancer Res Treat. 2016;48:687–97. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.320. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sarkaria JN, Kitange GJ, James CD, Plummer R, Calvert H, Weller M, Wick W. Mechanisms of chemoresistance to alkylating agents in malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2900–8. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-1719. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caporali S, Levati L, Starace G, Ragone G, Bonmassar E, Alvino E, D’Atri S. AKT is activated in an ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3-related-dependent manner in response to temozolomide and confers protection against drug-induced cell growth inhibition. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74:173–83. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.107.044743. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, Hau P, Brandes AA, Gijtenbeek J, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

