Genomic landscape of colitis-associated cancer indicates the impact of chronic inflammation and its stratification by mutations in the Wnt signaling
- PMID: 29416670
- PMCID: PMC5787528
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22867
Genomic landscape of colitis-associated cancer indicates the impact of chronic inflammation and its stratification by mutations in the Wnt signaling
Abstract
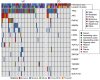
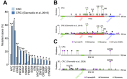
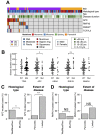
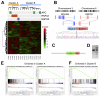
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) increases the risk of colorectal cancer, known as colitis-associated cancer (CAC). It is still unclear what driver mutations are caused by chronic inflammation and lead to CAC development. To get insight into this issue, we investigated somatic alterations in CAC. We performed exome sequencing of 22 fresh CACs and targeted sequencing of 43 genes on 90 archive specimens from Japanese CAC patients, of which 58 were ulcerative colitis (UC) and 32 were Crohn's disease (CD). Consistently with the previous reports, TP53 was commonly mutated (66%) whereas APC, KRAS and SMAD4 were mutated less frequently (16%, 11% and 11%, respectively). Mucinous CD-CACs in the anus, an Asian-specific subtype of CD-CAC, had less somatic mutations in our target genes. We also found that RNF43, a negative regulator of the Wnt signaling, was somatically mutated in a significant fraction of CACs (10 of 90; 11%). Two lines of evidence indicated that somatic mutations of RNF43 were related to chronic inflammation. First, somatic mutations of RNF43 were significantly associated with longer duration of IBD. Second, clinico-pathological features suggested many of the APC-mutated CACs were actually sporadic colorectal cancer whereas RNF43-mutated CACs did not have this tendency. RNA-Seq analysis showed that RNF43-mutated CACs had elevated expression of c-Myc and its target genes, suggesting that RNF43 is a bona fide driver of CAC development. This study provides evidence that somatic mutation of RNF43 is the driver genetic alteration that links chronic inflammation and cancer development in about 10% of CACs.
Keywords: APC; RNF43; colitis-associated cancer; inflammatory bowel disease; next-generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Berasain C, Castillo J, Perugorria MJ, Latasa MU, Prieto J, Avila MA. Inflammation and liver cancer: new molecular links. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1155:206–21. - PubMed
-
- Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M, Adami HO. Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. A population-based study. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1228–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

