Comparing the Efficacy of Low Dose and Conventional Dose of Oral Isotretinoin in Treatment of Moderate and Severe Acne Vulgaris
- PMID: 29417084
- PMCID: PMC5787910
- DOI: 10.4103/jrpp.JRPP_17_30
Comparing the Efficacy of Low Dose and Conventional Dose of Oral Isotretinoin in Treatment of Moderate and Severe Acne Vulgaris
Abstract
Objective: This study was conducted to compare the effect of low-dose isotretinoin with its conventional dose in patients with moderate and severe acne.
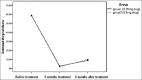
Methods: This was a clinical trial conducted on 60 male and female patients with moderate and severe acne vulgaris. The patients were divided into two treatment groups: 0.5 mg/kg/day isotretinoin capsule and low-dose isotretinoin capsule (0.25 mg/kg/day). Patients in both groups received 6-month treatment. At the end of the 6th month and 12th month (6 months after the end of the treatment), they were examined again, and their improvement was determined and compared.
Findings: The average severity of acne in the two treatment groups did not differ significantly within any of the study periods. The most common side effects were nose dryness in the low-dose group (17%) and hair thinning and loss in the conventional-dose group (33.2%), although all the patients had dry lips.
Conclusion: According to the same severity of the acne in two groups in different study periods, as well as fewer side effects and more patients' satisfaction, the low-dose isotretinoin can be considered in the treatment of acne.
Keywords: Acne vulgaris; Isotretinoin; efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Simpson NB, Cunliffe WJ. Disorders of the sebaceous glands. In: Burns T, Breathnaeh S, Cox N, Griffiths CH, editors. Rook Textbook of Dermatology. 7th ed. Blackwell Science: Massachusetts; 2004. pp. 17–43.
-
- Krug M, Wünsche A, Blum A. Addiction to tobacco and the consequences for the skin. Hautarzt. 2004;55:301–15. - PubMed
-
- Freiman A, Bird G, Metelitsa AI, Barankin B, Lauzon GJ. Cutaneous effects of smoking. J Cutan Med Surg. 2004;8:415–23. - PubMed
-
- Klaz I, Kochba I, Shohat T, Zarka S, Brenner S. Severe acne vulgaris and tobacco smoking in young men. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:1749–52. - PubMed
-
- Thiboutot DM. Overview of acne and its treatment. Cutis. 2008;81(1 Suppl):3–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources