Implementation of Steps 1-9 to Successful Breastfeeding Reduces the Frequency of Mild and Severe Episodes of Diarrhea and Respiratory Tract Infection Among 0-6 Month Infants in Democratic Republic of Congo
- PMID: 29417366
- PMCID: PMC6645680
- DOI: 10.1007/s10995-018-2446-9
Implementation of Steps 1-9 to Successful Breastfeeding Reduces the Frequency of Mild and Severe Episodes of Diarrhea and Respiratory Tract Infection Among 0-6 Month Infants in Democratic Republic of Congo
Abstract
Introduction: Global initiatives to improve breastfeeding practices have focused on the Ten Steps to Successful Breastfeeding. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of implementing Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI) steps 1-9 and BFHI steps 1-10 on incidence of diarrhea and respiratory illnesses in the first 6 months of life.
Methods: We reanalyzed a cluster randomized trial in which health-care clinics in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo, were randomly assigned to standard care (control group), BFHI steps 1-9, or BFHI steps 1-10. Outcomes included episodes of diarrhea and respiratory illness. Piecewise Poisson regression with generalized estimation equations to account for clustering by clinic was used to estimate incidence rate ratios (IRR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
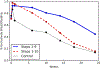
Results: Steps 1-9 was associated with a decreased incidence of reported diarrhea (IRR 0.72, 95% CI 0.53, 0.99) and respiratory illness (IRR 0.48, 95% CI 0.37, 0.63), health facility visits due to diarrhea (IRR 0.60, 95% CI 0.42, 0.85) and respiratory illness (IRR 0.47, 95% CI 0.36, 0.63), and hospitalizations due to diarrhea (IRR 0.42, 95% CI 0.17, 1.06) and respiratory illness (IRR 0.33, 95% CI 0.11, 0.98). Addition of Step 10 attenuated this effect: episodes of reported diarrhea (IRR 1.24, 95% CI 0.93, 1.68) and respiratory illness (IRR 0.77, 95% CI 0.60, 0.99), health facility visits due to diarrhea (IRR 0.76, 95% CI 0.54, 1.08) and respiratory illness (IRR 0.75 95% CI 0.57, 0.97), and hospitalizations due to respiratory illness (IRR 0.48 95% CI 0.16, 1.40); but strengthened the effect against hospitalizations due to diarrhea (IRR 0.14, 95% CI 0.03, 0.60).
Conclusions: Implementation of steps 1-9 significantly reduced incidence of mild and severe episodes of diarrhea and respiratory infection in the first 6 months of life, addition of step 10 appeared to lessen this effect.
Trial registration: NCT01428232.
Keywords: Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI).; Breastfeeding; Diarrhea; Infants; Respiratory illness.
Figures
References
-
- Hoddinott P, Craig L, Maclennan G, Boyers D, & Vale L (2012). The FEeding Support Team (FEST) randomised, controlled feasibility trial of proactive and reactive telephone support for breastfeeding women living in disadvantaged areas. BMJ Open, 2(2). doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000652 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 AI096299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 09-000076-AT11-123-UNC-DRC/Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation/International
- R01HD087993/National Institute of Child Health and Human Development/International
- U01AI096299-01/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/International
- R01 HD087993/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

