Structural prediction of protein models using distance restraints derived from cross-linking mass spectrometry data
- PMID: 29419816
- PMCID: PMC5999019
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2017.146
Structural prediction of protein models using distance restraints derived from cross-linking mass spectrometry data
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Structural prediction of protein models using distance restraints derived from cross-linking mass spectrometry data.Nat Protoc. 2018 Jul;13(7):1724. doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0024-7. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29942004
Abstract
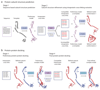
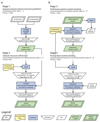
This protocol describes a workflow for creating structural models of proteins or protein complexes using distance restraints derived from cross-linking mass spectrometry experiments. The distance restraints are used (i) to adjust preliminary models that are calculated on the basis of a homologous template and primary sequence, and (ii) to select the model that is in best agreement with the experimental data. In the case of protein complexes, the cross-linking data are further used to dock the subunits to one another to generate models of the interacting proteins. Predicting models in such a manner has the potential to indicate multiple conformations and dynamic changes that occur in solution. This modeling protocol is compatible with many cross-linking workflows and uses open-source programs or programs that are free for academic users and do not require expertise in computational modeling. This protocol is an excellent additional application with which to use cross-linking results for building structural models of proteins. The established protocol is expected to take 6-12 d to complete, depending on the size of the proteins and the complexity of the cross-linking data.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures






Comment in
-
Defining distance restraints in HADDOCK.Nat Protoc. 2018 Jul;13(7):1503. doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0017-6. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29942005 No abstract available.
References
-
- Leitner A, Faini M, Stengel F, Aebersold R. Crosslinking and Mass Spectrometry: An Integrated Technology to Understand the Structure and Function of Molecular Machines. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41:20–32. - PubMed
-
- Holding AN. XL-MS: Protein cross-linking coupled with mass spectrometry. Methods. 2015;89:54–63. - PubMed
-
- Herzog F, et al. Structural probing of a protein phosphatase 2A network by chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometry. Science. 2012;337:1348–1352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

