Low-dose bevacizumab as an effective pre-treatment for peri-tumoral brain edema prior to CyberKnife radiosurgery: A case report
- PMID: 29420112
- PMCID: PMC5927660
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1433499
Low-dose bevacizumab as an effective pre-treatment for peri-tumoral brain edema prior to CyberKnife radiosurgery: A case report
Abstract
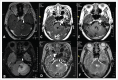
A 75-y-old Chinese female patient diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastasis suffered severe nausea and vomiting, and these symptoms were contraindications for CyberKnife treatment. Neither mannitol, nor dexamethasone, relieved the symptoms. However, after the patient received a single dose of bevacizumab (200 mg, 2.9 mg/kg), the patient's symptoms were significantly relieved. The patient subsequently completed a successful CyberKnife treatment. In addition, the patient received an oral treatment of gefitinib. At 15 months post treatment, the patient's brain tumor was controlled. Thus, administration of bevacizumab at a low dose (2.9 mg/kg) may significantly alleviate peri-tumoral brain edema and its symptoms, thereby facilitating radiosurgery treatment.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; bevacizumab; peri-tumoral brain edema; radiosurgery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new strategy of CyberKnife treatment system based radiosurgery followed by early use of adjuvant bevacizumab treatment for brain metastasis with extensive cerebral edema.J Neurooncol. 2014 Sep;119(2):369-76. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1488-0. Epub 2014 May 31. J Neurooncol. 2014. PMID: 24879376
-
Clinical Variables for Prediction of the Therapeutic Effects of Bevacizumab Monotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients With Radiation-Induced Brain Necrosis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018 Mar 1;100(3):621-629. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.11.023. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018. PMID: 29413276
-
Brain Radionecrosis Treated with Bevacizumab in a Patient with Resected Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung.J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Jan;12(1):e1-e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.08.124. Epub 2016 Aug 17. J Thorac Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27544055 No abstract available.
-
Bevacizumab in Cervical Cancer: 5 Years After.Cancer J. 2018 Jul/Aug;24(4):187-192. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000324. Cancer J. 2018. PMID: 30119082 Review.
-
Bevacizumab in advanced lung cancer: state of the art.Future Oncol. 2017 Dec;13(28):2515-2535. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0302. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Future Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28812378 Review.
Cited by
-
Dose and Efficacy of Bevacizumab in Recurrent High-Grade Gliomas: A Retrospective Study.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Nov 16;16:1617-1626. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S481289. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39575164 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Options for Brain Metastases in Gynecologic Cancers.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022 Nov;23(11):1601-1613. doi: 10.1007/s11864-022-01013-8. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36255665 Review.
References
-
- Lemercier P, Paz Maya S, Patrie JT, Flors L, Leiva-Salinas C. Gradient of apparent diffusion coefficient values in peritumoral edema helps in differentiation of glioblastoma from solitary metastatic lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203:163–169. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.11186. PMID:24951211. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palma L, Bruni G, Fiaschi AI, Mariottini A. Passage of mannitol into the brain around gliomas: a potential cause of rebound phenomenon. A study on 21 patients. J Neurosurg Sci. 2006;50:63–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
