The piRNA targeting rules and the resistance to piRNA silencing in endogenous genes
- PMID: 29420292
- PMCID: PMC5939965
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aao2840
The piRNA targeting rules and the resistance to piRNA silencing in endogenous genes
Abstract
Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) silence transposons to safeguard genome integrity in animals. However, the functions of the many piRNAs that do not map to transposons remain unknown. Here, we show that piRNA targeting in Caenorhabditis elegans can tolerate a few mismatches but prefer perfect pairing at the seed region. The broad targeting capacity of piRNAs underlies the germline silencing of transgenes in C. elegans Transgenes engineered to avoid piRNA recognition are stably expressed. Many endogenous germline-expressed genes also contain predicted piRNA targeting sites, and periodic An/Tn clusters (PATCs) are an intrinsic signal that provides resistance to piRNA silencing. Together, our study revealed the piRNA targeting rules and highlights a distinct strategy that C. elegans uses to distinguish endogenous from foreign nucleic acids.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
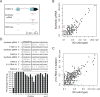

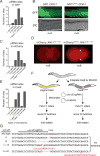
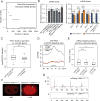
Comment in
-
piRNA Rules of Engagement.Dev Cell. 2018 Mar 26;44(6):657-658. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.03.006. Dev Cell. 2018. PMID: 29587140
References
-
- Brennecke J, et al. Discrete Small RNA-Generating Loci as Master Regulators of Transposon Activity in Drosophila. Cell. 2007;128:1089–1103. - PubMed
-
- Carmell MA, et al. MIWI2 Is Essential for Spermatogenesis and Repression of Transposons in the Mouse Male Germline. Developmental Cell. 2007;12:503–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

