Rapid Increase in Reports of Syphilis Associated With Men Who Have Sex With Women and Women Who Have Sex With Men, Japan, 2012 to 2016
- PMID: 29420439
- PMCID: PMC5815645
- DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000768
Rapid Increase in Reports of Syphilis Associated With Men Who Have Sex With Women and Women Who Have Sex With Men, Japan, 2012 to 2016
Abstract
Background: In Japan, syphilis reports have recently increased rapidly. However, unlike other developed countries where men who have sex with men (MSM) were associated with the rise, the increase in Japan has been attributed more to men who have sex with women (MSW) and women who have sex with men (WSM). We report on this increase based on surveillance data.
Methods: Syphilis is a notifiable disease requiring all laboratory-confirmed cases to be reported; stage and sex of the sex partner(s) suspected as the infection source are also reported. Focusing on primary and secondary (P&S) cases, we describe the temporal, demographic, and geographic distributions of reported cases in 2012 through 2016.
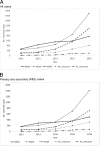
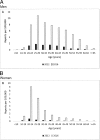
Results: A total of 7040 (64.0%) of 10,997 cases were P&S; the annual rate of increase was greatest for P&S and the proportion of P&S increased over time. Among P&S cases (1609 MSM, 2768 MSW, and 1323 WSM), MSW and WSM each surpassed MSM cases in 2016. Men were older with a wider age distribution (median, 37 years; interquartile range, 28-46 years) relative to women (median, 26 years; interquartile range, 21-34 years). Among women, 20- to 24-year-olds consistently had the highest reporting rate, reaching 9.0 per 100,000 in 2016. Congenital syphilis reports increased from 0.4 in 2012 to 1.4 per 100,000 live births in 2016. Although Tokyo prefecture had the highest reporting rate (3.98 per 100,000 person-years), the proportionate contribution from Tokyo decreased in 2016.
Conclusions: Reports on P&S syphilis increased yearly among MSW and WSM. Young women seem to be at particular risk, and with increased reports of congenital syphilis, syphilis prevention and control is currently a public health priority in Japan.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest and Source of Funding: All authors report no conflict of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Rapid Increases in Syphilis in Reproductive-Aged Women in Japan: A Warning for Other Countries?Sex Transm Dis. 2018 Mar;45(3):144-146. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000792. Sex Transm Dis. 2018. PMID: 29420440 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2015. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2016. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats15/default.htm Accessed July 30, 2017.
-
- Public Health England. Syphilis Epidemiology in London. London; August 17, 2016. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/syphilis-epidemiology-in-london Accessed July 30, 2017.
-
- Pinto-Sander N, Youssef E, Tweed M, et al. A significant increase in cases of infectious syphilis in men who have sex with men since November 2013. Int J STD AIDS 2016; 27:697–698. - PubMed
-
- Champenois K, Cousien A, Ndiaye B, et al. Risk factors for syphilis infection in men who have sex with men: Results of a case-control study in Lille, France. Sex Transm Infect 2013; 89:128–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

