The tumour microenvironment creates a niche for the self-renewal of tumour-promoting macrophages in colon adenoma
- PMID: 29422500
- PMCID: PMC5805689
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-02834-8
The tumour microenvironment creates a niche for the self-renewal of tumour-promoting macrophages in colon adenoma
Abstract
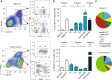
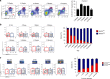
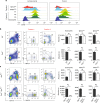
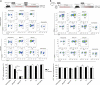
Circulating CCR2+ monocytes are crucial for maintaining the adult tissue-resident F4/80hiMHCIIhi macrophage pool in the intestinal lamina propria. Here we show that a subpopulation of CCR2-independent F4/80hiMHCIIlow macrophages, which are the most abundant F4/80hi cells in neonates, gradually decline in number in adulthood; these macrophages likely represent the fetal contribution to F4/80hi cells. In colon adenomas of ApcMin/+ mice, F4/80hiMHCIIlow macrophages are not only preserved, but become the dominant subpopulation among tumour-resident macrophages during tumour progression. Furthermore, these pro-tumoural F4/80hiMHCIIlow and F4/80hiMHCIIhi macrophages can self-renew in the tumour and maintain their numbers mostly independent from bone marrow contribution. Analyses of colon adenomas indicate that CSF1 may be a key facilitator of macrophage self-renewal. In summary, the tumour microenvironment creates an isolated niche for tissue-resident macrophages that favours macrophage survival and self-renewal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CSF-1-dependent red pulp macrophages regulate CD4 T cell responses.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):2229-37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001345. Epub 2011 Jan 14. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21239712
-
Long-lived self-renewing bone marrow-derived macrophages displace embryo-derived cells to inhabit adult serous cavities.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 13;7:ncomms11852. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11852. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27292029 Free PMC article.
-
The Kidney Contains Ontogenetically Distinct Dendritic Cell and Macrophage Subtypes throughout Development That Differ in Their Inflammatory Properties.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Feb;31(2):257-278. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019040419. Epub 2020 Jan 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31932472 Free PMC article.
-
Self-renewing resident cardiac macrophages limit adverse remodeling following myocardial infarction.Nat Immunol. 2019 Jan;20(1):29-39. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0272-2. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Nat Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30538339 Free PMC article.
-
[Niche signals regulate differentiation and functions of tissue resident macrophages].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2018;59(10):1886-1894. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.59.1886. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2018. PMID: 30305489 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Hydrogel platform with tunable stiffness based on magnetic nanoparticles cross-linked GelMA for cartilage regeneration and its intrinsic biomechanism.Bioact Mater. 2022 Jul 30;25:615-628. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.07.013. eCollection 2023 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 37056264 Free PMC article.
-
Functionally and Metabolically Divergent Melanoma-Associated Macrophages Originate from Common Bone-Marrow Precursors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 24;15(13):3330. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133330. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444440 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of synovial macrophage metabolism by synovial fibroblasts under inflammatory conditions.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Nov 30;18(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00678-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 33256735 Free PMC article.
-
27-Hydroxycholesterol acts on myeloid immune cells to induce T cell dysfunction, promoting breast cancer progression.Cancer Lett. 2020 Nov 28;493:266-283. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.08.020. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32861706 Free PMC article.
-
Hematologic dysfunction in cancer: Mechanisms, effects on antitumor immunity, and roles in disease progression.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 6;13:1041010. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1041010. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36561751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

