Processivity and enzymatic mechanism of a multifunctional family 5 endoglucanase from Bacillus subtilis BS-5 with potential applications in the saccharification of cellulosic substrates
- PMID: 29422948
- PMCID: PMC5787917
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-018-1022-2
Processivity and enzymatic mechanism of a multifunctional family 5 endoglucanase from Bacillus subtilis BS-5 with potential applications in the saccharification of cellulosic substrates
Abstract
Background: Presently, enzymes still constitute a major part of the cost of biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass. Processive endoglucanases, which possess both endoglucanase and exoglucanase activity, have the potential to reduce the costs of biomass saccharification when used together with commercial cellulases. Therefore, the exploration of new processive endoglucanases has attracted much attention with a view to accelerating the industrialization of biofuels and biochemicals.
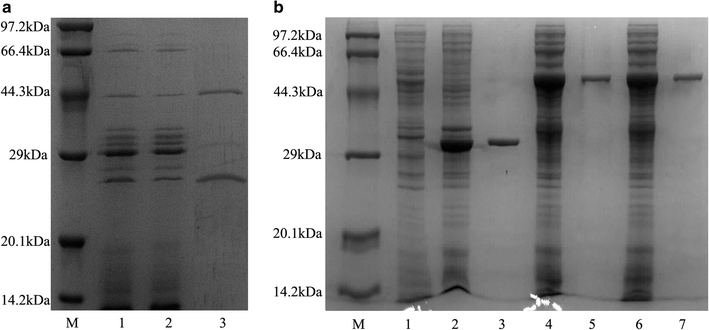
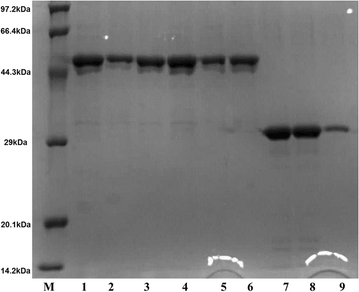
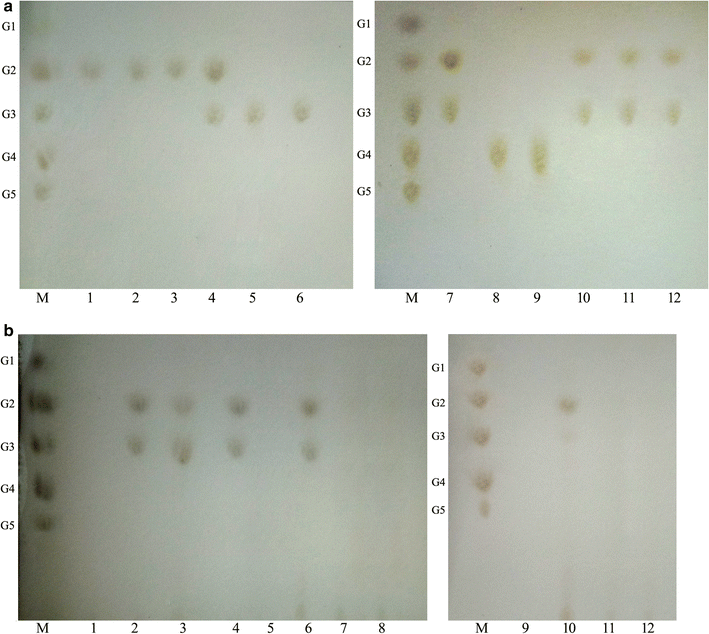
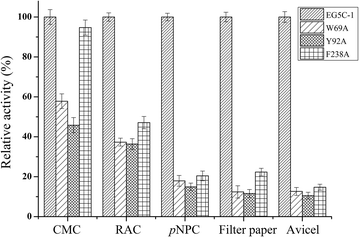
Results: The endoglucanase EG5C and its truncated form EG5C-1 from Bacillus subtilis BS-5 were expressed and characterized. EG5C was a typical endoglucanase, comprised of a family 5 catalytic domain and family 3 carbohydrate-binding domain, and which had high activity toward soluble cellulosic substrates, but low activity toward insoluble cellulosic substrates. Importantly, the truncated form EG5C-1 was a processive endoglucanase that hydrolyzed not only carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), but also insoluble cellulosic substrates. The hydrolytic activities of EG5C-1 towards CMC, phosphoric acid-swollen cellulose (PASC), p-nitrophenyl-β-d-cellobioside, filter paper and Avicel are 4170, 700, 2550, 405 and 320 U/μmol, respectively. These data demonstrated that EG5C-1 had higher activity ratio of exoglucanase to endoglucanase than other known processive endoglucanases. When PASC was degraded by EG5C-1, the ratio of soluble to insoluble reducing sugars was about 3.7 after 3 h of incubation with cellobiose and cellotriose as the main products. Importantly, EG5C-1 alone was able to hydrolyze filter paper and PASC. At 5% substrate concentration and 10 FPU/g PASC enzyme loading, the saccharification yield was 76.5% after 60 h of incubation. Replacement of a phenylalanine residue (F238) by an alanine at the entrance/exit of the substrate binding cleft significantly reduces the ability of EG5C-1 to degrade filter paper and Avicel, but this mutation has little impact on CMCase activity. The processivity of this mutant was also greatly reduced while its cellulose binding ability was markedly enhanced.
Conclusions: The processive endoglucanase EG5C-1 from B. subtilis BS-5 exhibits excellent properties that render it a suitable candidate for use in biofuel and biochemical production from lignocellulosic biomass. In addition, our studies also provide useful information for research on enzyme processivity at the molecular level.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; Family 5 glycoside hydrolase; Multifunctional; Processive endoglucanase; Saccharification.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A processive GH9 family endoglucanase of Bacillus licheniformis and the role of its carbohydrate-binding domain.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;106(18):6059-6075. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12117-4. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35948851
-
Enhancing the catalytic activity of a GH5 processive endoglucanase from Bacillus subtilis BS-5 by site-directed mutagenesis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jan 31;168:442-452. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.060. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33310097
-
Structure-Guided Engineering Unveils Deeper Substrate Channel in Processive Endoglucanase EG5C-1 Contributing to Enhanced Catalytic Efficiency and Processivity.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Dec 20;13(12):4131-4142. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00562. Epub 2024 Nov 23. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 39579149
-
Processivity and the Mechanisms of Processive Endoglucanases.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;190(2):448-463. doi: 10.1007/s12010-019-03096-w. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31378843 Review.
-
Superhydrophobic modification of cellulosic paper-based materials: Fabrication, properties, and versatile applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2023 Apr 1;305:120570. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120570. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Carbohydr Polym. 2023. PMID: 36737208 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the Correlation between Persimmon Fruit-Sugar Components and Taste Traits from Germplasm Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 16;25(14):7803. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147803. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063045 Free PMC article.
-
Production, Purification, and Characterization of a Cellulase from Paenibacillus elgii.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jul 17;16(14):2037. doi: 10.3390/polym16142037. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065354 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of hydrolysis modes among xylanases reveals the mechanism of hemicellulose hydrolysis by Penicillium chrysogenum P33.Microb Cell Fact. 2019 Sep 21;18(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1212-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2019. PMID: 31542050 Free PMC article.
-
A processive GH9 family endoglucanase of Bacillus licheniformis and the role of its carbohydrate-binding domain.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;106(18):6059-6075. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12117-4. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35948851
-
Multifunctional cellulases are potent, versatile tools for a renewable bioeconomy.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021 Feb;67:141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2020.12.020. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33550093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

