LED enhances anti-inflammatory effect of luteolin (3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) in vitro
- PMID: 29423013
- PMCID: PMC5801366
LED enhances anti-inflammatory effect of luteolin (3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) in vitro
Abstract
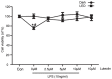
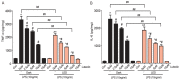
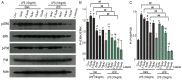
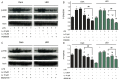
Neuroinflammation is a complex pathological process usually results from abnormal microglial activation, thus, intervention in a microglial stimulation pathway could be a promising approach for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Luteolin is an important bioflavonoid possesses anti-inflammatory properties, which is widely studied over these years. Light emitting diode (LED) therapy is reported to be a potential therapeutic strategy for many diseases including neurodegenerative diseases. However, little is known about the anti-inflammatory effect of LED therapy on activated microglial cells, even less is known whether there is a synergistic anti-inflammatory effect exist in LED and luteolin therapy. In this study, we aimed to confirm the anti-inflammatory effect of luteolin and LED combination therapy in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. We showed that luteolin inhibited LPS-induced cytotoxicity, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) production through modulation of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling in BV2 cells. In addition, LED therapy enhanced the anti-inflammatory effect of luteolin. These results suggest that a synergistic effect between luteolin and LED could be a new effective therapy in relieving neuroinflammation.
Keywords: ERK; IL-6; LED; Neuroinflammation; TNFα; luteolin; p38.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Luteolin inhibits cytokine expression in endotoxin/cytokine-stimulated microglia.J Nutr Biochem. 2011 Jul;22(7):612-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.01.011. Epub 2010 Oct 30. J Nutr Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21036586
-
A synthetic diosgenin primary amine derivative attenuates LPS-stimulated inflammation via inhibition of NF-κB and JNK MAPK signaling in microglial BV2 cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Aug;61:204-214. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.05.021. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29890414
-
Luteolin reduces primary hippocampal neurons death induced by neuroinflammation.Neurol Res. 2011 Nov;33(9):927-34. doi: 10.1179/1743132811Y.0000000023. Neurol Res. 2011. PMID: 22080993
-
Apigenin and luteolin modulate microglial activation via inhibition of STAT1-induced CD40 expression.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Sep 25;5:41. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-41. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18817573 Free PMC article.
-
Steppogenin Isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata Shows Antineuroinflammatory Effects via NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV2 and Primary Rat Microglial Cells.Molecules. 2017 Dec 2;22(12):2130. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122130. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29207498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dheen ST, Kaur C, Ling EA. Microglial activation and its implications in the brain diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2007;14:1189–1197. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
