Therapeutic effect of nerve growth factor on canine cerebral infarction evaluated by MRI
- PMID: 29423079
- PMCID: PMC5790496
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23345
Therapeutic effect of nerve growth factor on canine cerebral infarction evaluated by MRI
Abstract
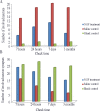
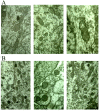
To explore therapeutic effect of nerve growth factor (NGF) on cerebral infarction by establishing canine middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) infarct model. The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology was used to study effects of NGF on cerebral infarction, and the results of MRI indexes (such as diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI)) were compared with the results of pathology, cell biology and molecular biology. The clinical manifestations of the canine infarction model treated by NGF were significantly improved within 7 days compared with control group. The therapeutic evaluation of NGF effect could be determine by canine cerebral infarction treated by NGF within 6 hours according to DWI and PWI. From 6 hours to 7 days, therapeutic evaluation of NGF could be determine by T1WI, T2WI and FLAIR. DWI and PWI could find the change of cerebral ischemia at the early stage, provide advantages for qualitative diagnosis of early-stage cerebral infarction and observation of efficacy in early treatment, initially showing that their great potential for NGF role on cerebral ischemia and mechanism.
Keywords: canine middle cerebral artery occlusion; diffusion-weighted imaging; magnetic resonance imaging; nerve growth factor; perfusion-weighted imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors report no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wang Z, Xia Y, Zhao Y, Chen L, Zhu Y. Intestinal gutsfeature and role of apoE and glucose metabolism in cerebral infarction patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017;10:561–565.
-
- Cuello AC. Nerve Growth Factor. Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology. 2015:1–9.
-
- Zhao HM, Liu XF, Mao XW, Chen CF. Intranasal delivery of nerve growth factor to protect the central nervous system against acute cerebral infarction. Chin Med Sci J. 2004;19:257–261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

